Neuroinflammation and disruption in working memory in aged mice after acute stimulation of the peripheral innate immune system
- PMID: 17951027
- PMCID: PMC2374919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.08.014
Neuroinflammation and disruption in working memory in aged mice after acute stimulation of the peripheral innate immune system
Abstract
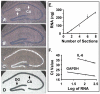
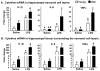
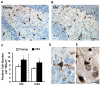
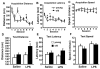
Acute cognitive disorders are common in elderly patients with peripheral infections but it is not clear why. Here, we injected old and young mice with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to mimic an acute peripheral infection and separated the hippocampal neuronal cell layers from the surrounding hippocampal tissue by laser capture microdissection and measured mRNA for several inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 beta, IL-6, and TNFalpha) that are known to disrupt cognition. The results showed that old mice had an increased inflammatory response in the hippocampus after LPS compared to younger cohorts. Immunohistochemistry further showed more microglial cells in the hippocampus of old mice compared to young adults, and that more IL-1 beta-positive cells were present in the dentate gyrus and in the CA1, CA2, and CA3 regions of LPS-treated old mice compared to young adults. In a test of cognition that required animals to effectively integrate new information with a preexisting schema to complete a spatial task, we found that hippocampal processing is more easily disrupted in old animals than in younger ones when the peripheral innate immune system is stimulated. Collectively, the results suggest that aging can facilitate neurobehavioral complications associated with peripheral infections probably by allowing the over expression of inflammatory cytokines in brain areas that mediate cognitive processing.
Figures

Comment in
-
The risky business of ageing.Brain Behav Immun. 2008 Mar;22(3):299-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2007.10.008. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Brain Behav Immun. 2008. PMID: 18042344
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 facilitates lipopolysaccharide-induced disruption in working memory and expression of other proinflammatory cytokines in hippocampal neuronal cell layers.J Neurosci. 2006 Oct 18;26(42):10709-16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3376-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17050710 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive deficits in interleukin-10-deficient mice after peripheral injection of lipopolysaccharide.Brain Behav Immun. 2009 Aug;23(6):794-802. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.02.020. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2009. PMID: 19272439 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin inhibits microglia and alters hippocampal-dependent spatial working memory in aged mice.J Nutr. 2010 Oct;140(10):1892-8. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.123273. Epub 2010 Aug 4. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20685893 Free PMC article.
-
Consuming a diet supplemented with resveratrol reduced infection-related neuroinflammation and deficits in working memory in aged mice.Rejuvenation Res. 2009 Dec;12(6):445-53. doi: 10.1089/rej.2009.0888. Rejuvenation Res. 2009. PMID: 20041738 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge promotes microglial hyperactivity in aged mice that is associated with exaggerated induction of both pro-inflammatory IL-1beta and anti-inflammatory IL-10 cytokines.Brain Behav Immun. 2009 Mar;23(3):309-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.09.002. Epub 2008 Sep 12. Brain Behav Immun. 2009. PMID: 18814846 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Common Protective Strategies in Neurodegenerative Disease: Focusing on Risk Factors to Target the Cellular Redox System.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Aug 1;2020:8363245. doi: 10.1155/2020/8363245. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32832006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Administration of red ginseng ameliorates memory decline in aged mice.J Ginseng Res. 2015 Jul;39(3):250-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Jan 22. J Ginseng Res. 2015. PMID: 26199557 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep and immunity: A growing field with clinical impact.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Jul;47:1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.03.011. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25849976 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Intracisternal administration of an interleukin-6 receptor antagonist attenuates surgery-induced cognitive impairment by inhibition of neuroinflammatory responses in aged rats.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Mar;9(3):982-986. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.2149. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Exp Ther Med. 2015. Retraction in: Exp Ther Med. 2023 Dec 05;27(2):49. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12333. PMID: 25667664 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Efficacy of a vegetal mixture composed of Zingiber officinale, Echinacea purpurea, and Centella asiatica in a mouse model of neuroinflammation: In vivo and ex vivo analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 30;9:887378. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.887378. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36118773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubert A, Vega C, Dantzer R, Goodall G. Pyrogens specifically disrupt the acquisition of a task involving cognitive processing in the rat. Brain Behav Immun. 1995;9:129–148. - PubMed
-
- Avital A, Goshen I, Kamsler A, Segal M, Iverfeldt K, Richter-Levin G, Yirmiya R. Impaired interleukin-1 signaling is associated with deficits in hippocampal memory processes and neural plasticity. Hippocampus. 2003;13:826–834. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Biedenkapp JC, Sprunger DB, Wright-Hardesty KJ, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Peripheral infection and aging interact to impair hippocampal memory consolidation. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:723–732. - PubMed
-
- Bellinger FP, Madamba S, Siggins GR. Interleukin 1 beta inhibits synaptic strength and long-term potentiation in the rat CA1 hippocampus. Brain Res. 1993;628:227–234. - PubMed
-
- Berg BM, Godbout JP, Kelley KW, Johnson RW. Alpha-tocopherol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness behavior in mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2004;18:149–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

