Variable prostaglandin E2 resistance in fibroblasts from patients with usual interstitial pneumonia
- PMID: 17916807
- PMCID: PMC2176116
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200706-963OC
Variable prostaglandin E2 resistance in fibroblasts from patients with usual interstitial pneumonia
Abstract
Rationale: Prostaglandin (PG) E2, a cyclooxygenase-derived lipid mediator, is a potent down-regulator of fibroblast activation in normal lung fibroblasts. Although fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are known to exhibit a defect in PGE2 synthesis, there is little information about their responsiveness to this lipid mediator.
Objectives: To compare responses to PGE2 in normal, usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), and other diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD) fibroblasts.
Methods: Fibroblasts were grown in vitro from well characterized control (n = 7), UIP (n = 17), or other DPLD (n = 13) lung tissue. The effects of PGE2 on fibroblast proliferation and collagen expression were determined.
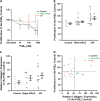
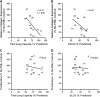
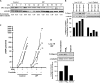
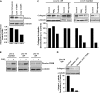
Measurements and main results: Only 3 of 12 UIP fibroblast lines exhibited PGE2-mediated inhibition of both collagen synthesis and cell proliferation, as opposed to 6 of 6 nonfibrotic control cell lines. The degree of PGE2 resistance in DPLD fibroblasts was quite variable, with UIP cells exhibiting the greatest degree of resistance to PGE2, whereas other DPLD fibroblasts manifested a degree of resistance intermediate to control and UIP. The resistance to suppression of collagen expression correlated with worse lung function. Molecular mechanisms for resistance included altered E prostanoid receptor profiles and diminished expression of the downstream kinase, protein kinase A.
Conclusions: The recognition that UIP fibroblasts manifest variable refractoriness to PGE2 suppression sheds new light on the activation phenotype of these cells and on the pathogenesis of fibrotic lung disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proliferative characteristics of fibroblast lines derived from open lung biopsy specimens of patients with IPF (UIP).Chest. 1992 Sep;102(3):832-7. doi: 10.1378/chest.102.3.832. Chest. 1992. PMID: 1516411
-
[Proliferative characteristics of fibroblast lines derived from open lung biopsy specimens of patients with the usual interstitial pneumonia form of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis].Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1991 Sep;29(9):1143-9. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1991. PMID: 1753541 Japanese.
-
Epigenetic regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by methylation of c8orf4 in pulmonary fibrosis.Clin Sci (Lond). 2016 Apr;130(8):575-86. doi: 10.1042/CS20150697. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26744410 Free PMC article.
-
Different effects of growth factors on proliferation and matrix production of normal and fibrotic human lung fibroblasts.Lung. 2005 Jul-Aug;183(4):225-37. doi: 10.1007/s00408-004-2534-z. Lung. 2005. PMID: 16211459 Review.
-
Pathogenetic mechanisms in usual interstitial pneumonia/idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.J Pathol. 2003 Nov;201(3):343-54. doi: 10.1002/path.1446. J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14595745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alveolar lipids in pulmonary disease. A review.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jun 3;19(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01278-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32493486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandin E₂ increases fibroblast gene-specific and global DNA methylation via increased DNA methyltransferase expression.FASEB J. 2012 Sep;26(9):3703-14. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-203323. Epub 2012 May 29. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22645246 Free PMC article.
-
Matrices of physiologic stiffness potently inactivate idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Apr;48(4):422-30. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0335OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23258227 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Airway remodeling in murine asthma correlates with a defect in PGE2 synthesis by lung fibroblasts.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Nov;301(5):L636-44. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00158.2011. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21873451 Free PMC article.
-
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 deficiency exacerbates pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in mice.Molecules. 2014 Apr 21;19(4):4967-85. doi: 10.3390/molecules19044967. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24756129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:1301–1315. - PubMed
-
- Bjoraker JA, Ryu JH, Edwin MK, Myers JL, Tazelaar HD, Schroeder DR, Offord KP. Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:199–203. - PubMed
-
- Myers JL, Katzenstein AL. Epithelial necrosis and alveolar collapse in the pathogenesis of usual interstitial pneumonia. Chest 1988;94:1309–1311. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn C III, Boldt J, King TE Jr, Crouch E, Vartio T, McDonald JA. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989;140:1693–1703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

