RNA editing of the human herpesvirus 8 kaposin transcript eliminates its transforming activity and is induced during lytic replication
- PMID: 17913828
- PMCID: PMC2168827
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01521-07
RNA editing of the human herpesvirus 8 kaposin transcript eliminates its transforming activity and is induced during lytic replication
Abstract
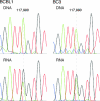
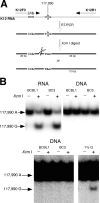
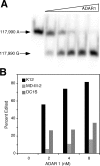
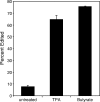
Human herpesvirus 8 is the etiologic agent associated with Kaposi's sarcoma and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). The K12 RNA, which produces as many as three variants of the kaposin protein, as well as a microRNA, is the most abundant transcript expressed in latent Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection, and yet it is also induced during lytic replication. The portion of the transcript that includes the microRNA and the kaposin A sequence has been shown to have tumorigenic potential. Genome coordinate 117990, which is within this transcript, has been found to be heterogeneous, primarily in RNAs but also among viral DNA sequences. This sequence heterogeneity affects an amino acid in kaposins A and C and the microRNA. The functional effects of this sequence heterogeneity have not been studied, and its origin has not been definitively settled; both RNA editing and heterogeneity at the level of the viral genome have been proposed. Here, we show that transcripts containing A at position 117990 are tumorigenic, while those with G at this position are not. Using a highly sensitive quantitative assay, we observed that, in PEL cells under conditions where more than 60% of cDNAs derived from K12 RNA transcripts have G at coordinate 117990, there is no detectable G in the viral DNA sequence at this position, only A. This result is consistent with RNA editing by one of the host RNA adenosine deaminases (ADARs). Indeed, we observed that purified human ADAR1 efficiently edits K12 RNA in vitro. Remarkably, the amount of editing correlated with the replicative state of the virus; editing levels were nearly 10-fold higher in cells treated to induce lytic viral replication. These results suggest that RNA editing controls the function of one segment of the kaposin transcript, such that it has transforming activity during latent replication and possibly another, as-yet-undetermined, function during lytic replication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the human herpesvirus 8 (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus) oncogene, kaposin (ORF K12).J Clin Virol. 2000 May;16(3):203-13. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(99)00081-5. J Clin Virol. 2000. PMID: 10738139
-
Identification of kaposin (open reading frame K12) as a human herpesvirus 8 (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus) transforming gene.J Virol. 1998 Jun;72(6):4980-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.6.4980-4988.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9573267 Free PMC article.
-
A complex translational program generates multiple novel proteins from the latently expressed kaposin (K12) locus of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.J Virol. 1999 Jul;73(7):5722-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.7.5722-5730.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10364323 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV Genome Replication and Maintenance in Latency.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1045:299-320. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7230-7_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29896673 Review.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Genomic changes in Kaposi Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and their clinical correlates.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Nov 28;18(11):e1010524. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010524. eCollection 2022 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36441790 Free PMC article.
-
It's the Little Things (in Viral RNA).mBio. 2020 Sep 15;11(5):e02131-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02131-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32934087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus microRNAs.Front Microbiol. 2012 May 3;3:165. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00165. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22563327 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine deaminase ADAR1 increases gene expression at the translational level by decreasing protein kinase PKR-dependent eIF-2alpha phosphorylation.J Mol Biol. 2009 Nov 6;393(4):777-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.08.070. Epub 2009 Sep 3. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19733181 Free PMC article.
-
Viral latency and its regulation: lessons from the gamma-herpesviruses.Cell Host Microbe. 2010 Jul 22;8(1):100-15. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.06.014. Cell Host Microbe. 2010. PMID: 20638646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arvanitakis, L., E. A. Mesri, R. G. Nador, J. W. Said, A. S. Asch, D. M. Knowles, and E. Cesarman. 1996. Establishment and characterization of a primary effusion (body cavity-based) lymphoma cell line (BC-3) harboring Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) in the absence of Epstein-Barr virus. Blood 88:2648-2654. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla, T., J. J. Rosenthal, M. Holmgren, and R. Reenan. 2004. Control of human potassium channel inactivation by editing of a small mRNA hairpin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11:950-956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

