Where is VEGF in the body? A meta-analysis of VEGF distribution in cancer
- PMID: 17912242
- PMCID: PMC2360423
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603923
Where is VEGF in the body? A meta-analysis of VEGF distribution in cancer
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a major target for the inhibition of tumour vascularisation and the treatment of human cancer. Many tumours produce large quantities of VEGF, and as a result, diagnosis and prognosis of cancer may be predicted by measuring changes in VEGF concentrations in blood. In blood, the VEGF may be located in the plasma, or in the blood-borne cells and formed elements, in particular, platelets and leukocytes. In this study, we collate the measurements of VEGF in platelets, leukocytes, plasma and serum for breast, prostate, colorectal and other cancers. In addition, we analysed the concentration of VEGF in tumour tissue itself, as well as for other tissues in the human body. Although the concentration of VEGF in tumours is high, the size of tumours is small compared to other tissues, in particular, skeletal muscle. Thus, the total quantity of VEGF in tumours and in blood is small compared to the quantity in muscles. This large reservoir of VEGF may have important implications for the treatment of cancer.
Figures

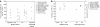
Similar articles
-
Alteration of protein expression pattern of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from soluble to cell-associated isoform during tumourigenesis.BMC Cancer. 2005 Oct 4;5:128. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-128. BMC Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16202150 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets and granulocytes, in particular the neutrophils, form important compartments for circulating vascular endothelial growth factor.Angiogenesis. 2003;6(4):283-7. doi: 10.1023/B:AGEN.0000029415.62384.ba. Angiogenesis. 2003. PMID: 15166496
-
The usefulness of determining the serum concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its soluble receptor type 2 (sVEGF-2) in the differential diagnosis of adrenal incidentalomas.Endokrynol Pol. 2012;63(1):22-8. Endokrynol Pol. 2012. PMID: 22378094
-
Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: the prognostic impact of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and blood.Lung Cancer. 2006 Feb;51(2):143-58. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.09.005. Epub 2005 Dec 19. Lung Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16360975 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a target of bevacizumab in cancer: from the biology to the clinic.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(16):1845-57. doi: 10.2174/092986706777585059. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842197 Review.
Cited by
-
First-in-human study of the anti-HB-EGF antibody U3-1565 in subjects with advanced solid tumors.Invest New Drugs. 2019 Feb;37(1):147-158. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0646-1. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Invest New Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30056611 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of preanalytical factors and methodological differences influencing the measurement of circulating vascular endothelial growth factor.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 6;17(7):e0270232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270232. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35793362 Free PMC article.
-
Increase of plasma VEGF after intravenous administration of bevacizumab is predicted by a pharmacokinetic model.Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 1;70(23):9886-94. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1419. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21118974 Free PMC article.
-
An observational study of plasma vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) A and D expression in non-localized prostate cancer.J Mens Health. 2012 Sep 1;9(3):182-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jomh.2012.04.003. J Mens Health. 2012. PMID: 24416090 Free PMC article.
-
Paxillin controls endothelial cell migration and tumor angiogenesis by altering neuropilin 2 expression.J Cell Sci. 2014 Apr 15;127(Pt 8):1672-83. doi: 10.1242/jcs.132316. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24522185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams J, Carder PJ, Downey S, Forbes MA, MacLennan K, Allgar V, Kaufman S, Hallam S, Bicknell R, Walker JJ, Cairnduff F, Selby PJ, Perren TJ, Lansdown M, Banks RE (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in breast cancer: comparison of plasma, serum, and tissue VEGF and microvessel density and effects of tamoxifen. Cancer Res 60: 2898–2905 - PubMed
-
- Bauer KS, Figg WD, Hamilton JM, Jones EC, Premkumar A, Steinberg SM, Dyer V, Linehan WM, Pluda JM, Reed E (1999) A pharmacokinetically guided Phase II study of carboxyamido-triazole in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 5: 2324–2329 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

