Cro's role in the CI Cro bistable switch is critical for {lambda}'s transition from lysogeny to lytic development
- PMID: 17908932
- PMCID: PMC1993876
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1584907
Cro's role in the CI Cro bistable switch is critical for {lambda}'s transition from lysogeny to lytic development
Abstract
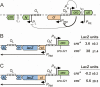
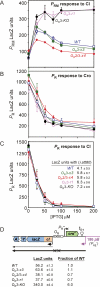
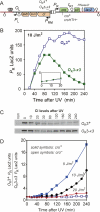
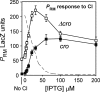
CI represses cro; Cro represses cI. This double negative feedback loop is the core of the classical CI-Cro epigenetic switch of bacteriophage lambda. Despite the classical status of this switch, the role in lambda development of Cro repression of the P(RM) promoter for CI has remained unclear. To address this, we created binding site mutations that strongly impaired Cro repression of P(RM) with only minimal effects on CI regulation of P(RM). These mutations had little impact on lambda development after infection but strongly inhibited the transition from lysogeny to the lytic pathway. We demonstrate that following inactivation of CI by ultraviolet treatment of lysogens, repression of P(RM) by Cro is needed to prevent synthesis of new CI that would otherwise significantly impede lytic development. Thus a bistable CI-Cro circuit reinforces the commitment to a developmental transition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of the lytic repressor in prophage induction of phage lambda as analyzed by a module-replacement approach.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 21;103(12):4558-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511117103. Epub 2006 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16537413 Free PMC article.
-
The Developmental Switch in Bacteriophage λ: A Critical Role of the Cro Protein.J Mol Biol. 2018 Jan 5;430(1):58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29158090 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of Cro in lambda prophage induction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Mar 22;102(12):4465-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409839102. Epub 2005 Feb 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15728734 Free PMC article.
-
Switches in bacteriophage lambda development.Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:409-29. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.39.073003.113656. Annu Rev Genet. 2005. PMID: 16285866 Review.
-
lambda Repressor and cro--components of an efficient molecular switch.Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):217-23. doi: 10.1038/294217a0. Nature. 1981. PMID: 6457992 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of residues in the N-terminal PAS domains important for dimerization of Arnt and AhR.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 May;39(9):3695-709. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1336. Epub 2011 Jan 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21245039 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting bistability in the lysis/lysogeny circuit of bacteriophage lambda.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 25;9(6):e100876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100876. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24963924 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing of Seven Strains of Staphylococcus lugdunensis Allows Identification of Mobile Genetic Elements.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 May 1;9(5). doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx077. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28444231 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that bacteriophage λ lysogens may induce in response to the proton motive force uncoupler CCCP.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016 Feb;363(3):fnv244. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv244. Epub 2015 Dec 23. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26705574 Free PMC article.
-
Using axenic and gnotobiotic insects to examine the role of different microbes on the development and reproduction of the kissing bug Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae).Mol Ecol. 2023 Feb;32(4):920-935. doi: 10.1111/mec.16800. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Mol Ecol. 2023. PMID: 36464913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhya S., Gottesman M., Gottesman M. Promoter occlusion: Transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell. 1982;29:939–944. - PubMed
-
- Baek K., Svenningsen S., Eisen H., Sneppen K., Brown S., Svenningsen S., Eisen H., Sneppen K., Brown S., Eisen H., Sneppen K., Brown S., Sneppen K., Brown S., Brown S. Single-cell analysis of λ immunity regulation. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;334:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Bailone A., Levine A., Devoret R., Levine A., Devoret R., Devoret R. Inactivation of prophage λ repressor in vivo. J. Mol. Biol. 1979;131:553–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
