RACK1 targets the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to link integrin engagement with focal adhesion disassembly and cell motility
- PMID: 17908799
- PMCID: PMC2169169
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00598-07
RACK1 targets the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway to link integrin engagement with focal adhesion disassembly and cell motility
Abstract
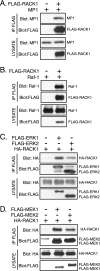
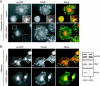
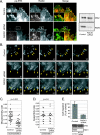
The extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) cascade is activated in response to a multitude of extracellular signals and converts these signals into a variety of specific biological responses, including cell differentiation, cell movement, cell division, and apoptosis. The specificity of the biological response is likely to be controlled in large measure by the localization of signaling, thus enabling ERK activity to be directed towards specific targets. Here we show that the RACK1 scaffold protein functions specifically in integrin-mediated activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK cascade and targets active ERK to focal adhesions. We found that RACK1 associated with the core kinases of the ERK pathway, Raf, MEK, and ERK, and that attenuation of RACK1 expression resulted in a decrease in ERK activity in response to adhesion but not in response to growth factors. RACK1 silencing also caused a reduction of active ERK in focal adhesions, an increase in focal adhesion length, a decreased rate of focal adhesion disassembly, and decreased motility. Our data further suggest that focal adhesion kinase is an upstream activator of the RACK1/ERK pathway. We suggest that RACK1 tethers the ERK pathway core kinases and channels signals from upstream activation by integrins to downstream targets at focal adhesions.
Figures

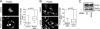

Similar articles
-
RACK1, an insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptor-interacting protein, modulates IGF-I-dependent integrin signaling and promotes cell spreading and contact with extracellular matrix.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):2345-65. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2345-2365.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884618 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of beta3-integrin gene expression by sustained activation of the Ras-regulated Raf-MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 May;21(9):3192-205. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.3192-3205.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11287623 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation during renal ischemia/reperfusion mediates focal adhesion dissolution and renal injury.Am J Pathol. 2007 Aug;171(2):452-62. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060805. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17620366 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical signals and biological responses elicited by the focal adhesion kinase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Jul 25;1540(1):1-21. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(01)00123-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11476890 Review.
-
Integrin-mediated signalling through the MAP-kinase pathway.IET Syst Biol. 2008 Jan;2(1):8-15. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb:20060058. IET Syst Biol. 2008. PMID: 18248081 Review.
Cited by
-
RACK1 enhances STAT3 stability and promotes T follicular helper cell development and function during blood-stage Plasmodium infection in mice.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jul 18;20(7):e1012352. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012352. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39024388 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous oncogenic KRAS expression increases cell proliferation and motility in near-diploid hTERT RPE-1 cells.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jun;300(6):107409. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107409. Epub 2024 May 23. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38796063 Free PMC article.
-
The c-Abl-RACK1-FAK signaling axis promotes renal fibrosis in mice through regulating fibroblast-myofibroblast transition.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 30;22(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01603-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38689280 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Trichinella spiralis serine proteinase disrupted gut epithelial barrier and mediated larval invasion through binding to RACK1 and activating MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Jan 8;18(1):e0011872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011872. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38190388 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RACK1 to alleviate TDP-43 and FUS proteinopathy-mediated suppression of protein translation and neurodegeneration.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Dec 18;11(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01705-8. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 38111057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carragher, N. O., M. A. Westhoff, V. J. Fincham, M. D. Schaller, and M. C. Frame. 2003. A novel role for FAK as a protease-targeting adaptor protein: regulation by p42 ERK and Src. Curr. Biol. 13:1442-1450. - PubMed
-
- Chang, L., and M. Karin. 2001. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410:37-40. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary, A., W. G. King, M. D. Mattaliano, J. A. Frost, B. Diaz, D. K. Morrison, M. H. Cobb, M. S. Marshall, and J. S. Brugge. 2000. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulates Raf1 through Pak phosphorylation of serine 338. Curr. Biol. 10:551-554. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Q., M. S. Kinch, T. H. Lin, K. Burridge, and R. L. Juliano. 1994. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion activates mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 269:26602-26605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
