Progranulin mediates caspase-dependent cleavage of TAR DNA binding protein-43
- PMID: 17898224
- PMCID: PMC6673167
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3421-07.2007
Progranulin mediates caspase-dependent cleavage of TAR DNA binding protein-43
Abstract
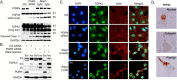
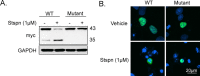
TAR DNA binding protein-43 (TDP-43) is the pathologic substrate of neuronal and glial inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions (FTDL-U) and in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Mutations in the progranulin gene (PGRN) have been shown to cause familial FTLD-U. The relationship between progranulin and TDP-43 and their respective roles in neurodegeneration is unknown. We report that progranulin mediates proteolytic cleavage of TDP-43 to generate approximately 35 and approximately 25 kDa species. Suppression of PGRN expression with small interfering RNA leads to caspase-dependent accumulation of TDP-43 fragments that can be inhibited with caspase inhibitor treatment. Cells treated with staurosporine also induced caspase-dependent cleavage and redistribution of TDP-43 from its nuclear localization to cytoplasm. Altered cleavage and redistribution of TDP-43 in cell culture models are similar to findings in FTLD-U and ALS. The results suggest that abnormal metabolism of TDP-43 mediated by progranulin may play a pivotal role in neurodegeneration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aberrant cleavage of TDP-43 enhances aggregation and cellular toxicity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 May 5;106(18):7607-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900688106. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19383787 Free PMC article.
-
Fine structural analysis of the neuronal inclusions of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 proteinopathy.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2008 Dec;115(12):1661-71. doi: 10.1007/s00702-008-0137-1. Epub 2008 Oct 31. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2008. PMID: 18974920 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Progranulin Expression Leads to Formation of Intranuclear TDP-43 Inclusions In Vitro: A Cell Model of Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2019 Dec 1;78(12):1124-1129. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlz102. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31626287
-
[Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and genetic mutations including progranulin gene].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2008 Nov;48(11):990-3. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.48.990. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2008. PMID: 19198141 Review. Japanese.
-
The genetics of frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007 Sep;7(5):434-42. doi: 10.1007/s11910-007-0067-6. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007. PMID: 17764635 Review.
Cited by
-
Robust cytoplasmic accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 in transgenic models of tauopathy.Acta Neuropathol. 2013 Jul;126(1):39-50. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1123-8. Epub 2013 May 11. Acta Neuropathol. 2013. PMID: 23666556 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin promotes peripheral nerve regeneration and reinnervation: role of notch signaling.Mol Neurodegener. 2016 Oct 22;11(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0132-1. Mol Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 27770818 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal sensitivity to TDP-43 overexpression is dependent on timing of induction.Acta Neuropathol. 2012 Jun;123(6):807-23. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-0979-3. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Acta Neuropathol. 2012. PMID: 22539017 Free PMC article.
-
Progranulin prevents regulatory NK cell cytotoxicity against antiviral T cells.JCI Insight. 2019 Sep 5;4(17):e129856. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.129856. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31484831 Free PMC article.
-
A Drosophila model for TDP-43 proteinopathy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 16;107(7):3169-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0913602107. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker M, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown SM, Gass J, Rademakers R, Lindholm C, Snowden J, Adamson J, Sadovnick AD, Rollinson S, Cannon A, Dwosh E, Neary D, Melquist S, Richardson A, Dickson D, Berger Z, Eriksen J, Robinson T, Zehr C, et al. Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature. 2006;442:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E, Baralle FE. Characterization and functional implications of the RNA binding properties of nuclear factor TDP-43, a novel splicing regulator of CFTR exon 9. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36337–36343. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E, Brindisi A, Giombi M, Tisminetzky S, Ayala YM, Baralle FE. TDP-43 binds heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B through its C-terminal tail: an important region for the inhibition of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator exon 9 splicing. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:37572–37584. - PubMed
-
- Cruts M, Gijselinck I, van der Zee J, Engelborghs S, Wils H, Pirici D, Rademakers R, Vandenberghe R, Dermaut B, Martin JJ, van Duijn C, Peeters K, Sciot R, Santens P, De Pooter T, Mattheijssens M, Van den Broeck M, Cuijt I, Vennekens K, De Deyn PP, et al. Null mutations in progranulin cause ubiquitin-positive frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17q21. Nature. 2006;442:920–924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
