The Arabidopsis homologs of trithorax (ATX1) and enhancer of zeste (CLF) establish 'bivalent chromatin marks' at the silent AGAMOUS locus
- PMID: 17881378
- PMCID: PMC2094062
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm464
The Arabidopsis homologs of trithorax (ATX1) and enhancer of zeste (CLF) establish 'bivalent chromatin marks' at the silent AGAMOUS locus
Erratum in
-
The Arabidopsis homologs of trithorax (ATX1) and enhancer of zeste (CLF) establish 'bivalent chromatin marks' at the silent AGAMOUS locus.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Apr 20;44(7):3475-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1489. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26673722 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
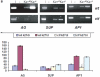
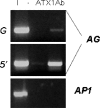
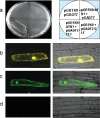
Tightly balanced antagonism between the Polycomb group (PcG) and the Trithorax group (TrxG) complexes maintain Hox expression patterns in Drosophila and murine model systems. Factors belonging to the PcG/TrxG complexes control various processes in plants as well but whether they participate in mechanisms that antagonize, balance or maintain each other's effects at a particular gene locus is unknown. CURLY LEAF (CLF), an Arabidopsis homolog of enhancer of zeste (EZ) and the ARABIDOPSIS HOMOLOG OF TRITHORAX (ATX1) control the expression of the flower homeotic gene AGAMOUS (AG). Disrupted ATX1 or CLF function results in misexpression of AG, recognizable phenotypes and loss of H3K4me3 or H3K27me3 histone H3-tail marks, respectively. A novel idea suggested by our results here, is that PcG and TrxG complexes function as a specific pair generating bivalent chromatin marks at the silent AG locus. Simultaneous loss of ATX1 and CLF restored AG repression and normalized leaf phenotypes. At the molecular level, disrupted ATX1 and CLF functions did not lead to erasure of the CLF- and ATX1-generated epigenetic marks, as expected: instead, in the double mutants, H3K27me3 and H3K4me3 tags were partially restored. We demonstrate that ATX1 and CLF physically interact linking mechanistically the observed effects.
Figures


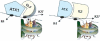
Similar articles
-
Trithorax Group Proteins Act Together with a Polycomb Group Protein to Maintain Chromatin Integrity for Epigenetic Silencing during Seed Germination in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant. 2018 May 7;11(5):659-677. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Mol Plant. 2018. PMID: 29428247
-
Methylation patterns of histone H3 Lys 4, Lys 9 and Lys 27 in transcriptionally active and inactive Arabidopsis genes and in atx1 mutants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Sep 12;33(16):5199-207. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki830. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16157865 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis homologs of trithorax (ATX1) and enhancer of zeste (CLF) establish 'bivalent chromatin marks' at the silent AGAMOUS locus.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Apr 20;44(7):3475-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1489. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26673722 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The complexity of PRC2 catalysts CLF and SWN in plants.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Dec 18;48(6):2779-2789. doi: 10.1042/BST20200660. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 33170267 Review.
-
Current understanding of plant Polycomb group proteins and the repressive histone H3 Lysine 27 trimethylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Aug 28;48(4):1697-1706. doi: 10.1042/BST20200192. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32725200 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene activation and cell fate control in plants: a chromatin perspective.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Aug;71(16):3119-37. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1609-0. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24714879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H2A.Z promotes the transcription of MIR156A and MIR156C in Arabidopsis by facilitating the deposition of H3K4me3.Development. 2018 Jan 25;145(2):dev152868. doi: 10.1242/dev.152868. Development. 2018. PMID: 29361556 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of H3K27me3 methylation and demethylation in plant development.Plant Signal Behav. 2015;10(9):e1027851. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2015.1027851. Plant Signal Behav. 2015. PMID: 26313233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic and co-expression analysis of OsSET gene family in rice.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 7;8(6):e65426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065426. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762371 Free PMC article.
-
TCO, a Putative Transcriptional Regulator in Arabidopsis, Is a Target of the Protein Kinase CK2.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 28;20(1):99. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010099. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30597831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grimaud C, Negre N, Cavalli G. From genetics to epigenetics: the tale of Polycomb group and trithorax group genes. Chromosome Res. 2006;14:363–375. - PubMed
-
- Ringrose L, Paro R. Epigenetic regulation of cellular memory by the Polycomb group and thrithorax group proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2004;38:413–443. - PubMed
-
- Francis NJ, Kingston RE, Woodcock CL. Chromatin compaction by a Polycomb group protein. Science. 2004;306:1574–1577. - PubMed
-
- Levine SS, King IFG, Kingston RE. Division of labor in Polycomb group repression. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004;29:478–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

