RluD, a highly conserved pseudouridine synthase, modifies 50S subunits more specifically and efficiently than free 23S rRNA
- PMID: 17872507
- PMCID: PMC2040082
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.711207
RluD, a highly conserved pseudouridine synthase, modifies 50S subunits more specifically and efficiently than free 23S rRNA
Abstract
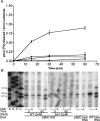
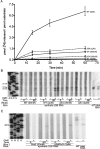
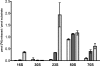
Pseudouridine modifications in helix 69 (H69) of 23S ribosomal RNA are highly conserved among all organisms. H69 associates with helix 44 of 16S rRNA to form bridge B2a, which plays a vital role in bridging the two ribosomal subunits and stabilizing the ribosome. The three pseudouridines in H69 were shown earlier to play an important role in 50S subunit assembly and in its association with the 30S subunit. In Escherichia coli, these three modifications are made by the pseudouridine synthase, RluD. Previous work showed that RluD is required for normal ribosomal assembly and function, and that it is the only pseudouridine synthase required for normal growth in E. coli. Here, we show that RluD is far more efficient in modifying H69 in structured 50S subunits, compared to free or synthetic 23S rRNA. Based on this observation, we suggest that pseudouridine modifications in H69 are made late in the assembly of 23S rRNA into mature 50S subunits. This is the first reported observation of a pseudouridine synthase being able to modify a highly structured ribonucleoprotein particle, and it may be an important late step in the maturation of 50S ribosomal subunits.
Figures
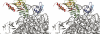
Similar articles
-
Substrate specificity of the pseudouridine synthase RluD in Escherichia coli.FEBS J. 2007 Nov;274(21):5759-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06101.x. Epub 2007 Oct 12. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 17937767
-
Specificity and kinetics of 23S rRNA modification enzymes RlmH and RluD.RNA. 2010 Nov;16(11):2075-84. doi: 10.1261/rna.2234310. Epub 2010 Sep 3. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20817755 Free PMC article.
-
The pseudouridine synthase RluD is required for normal ribosome assembly and function in Escherichia coli.RNA. 2005 Jul;11(7):1141-52. doi: 10.1261/rna.2550105. Epub 2005 May 31. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15928344 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudouridines and pseudouridine synthases of the ribosome.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:147-59. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.147. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762017 Review.
-
RNA-modifying enzymes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003 Feb;13(1):49-55. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00002-7. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12581659 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of RNA damage under oxidative stress in Escherichia coli.Biol Chem. 2012 Mar;393(3):123-32. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2011-0247. Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22718628 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudouridine: still mysterious, but never a fake (uridine)!RNA Biol. 2014;11(12):1540-54. doi: 10.4161/15476286.2014.992278. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 25616362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Genes Responsible for Adhesion to Chicken and Human Cell Lines.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Oct 1;86(20):e01068-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01068-20. Print 2020 Oct 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32769194 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of rRNA modifications using stable isotope labeling and mass spectrometry.J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Feb 5;136(5):2058-69. doi: 10.1021/ja412084b. Epub 2014 Jan 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 24422502 Free PMC article.
-
YbeA is the m3Psi methyltransferase RlmH that targets nucleotide 1915 in 23S rRNA.RNA. 2008 Oct;14(10):2234-44. doi: 10.1261/rna.1198108. Epub 2008 Aug 28. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18755835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali, I.K., Lancaster, L., Feinberg, J., Joseph, S., Noller, H.F. Deletion of a conserved, central ribosomal intersubunit RNA bridge. Mol. Cell. 2006;23:865–874. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, N.M., Douthwaite, S. YebU is a m5C methyltransferase specific for 16 S rRNA nucleotide 1407. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;359:777–786. - PubMed
-
- Bashan, A., Agmon, I., Zarivach, R., Schluenzen, F., Harms, J., Berisio, R., Bartels, H., Franceschi, F., Auerbach, T., Hansen, H.A., et al. Structural basis of the ribosomal machinery for peptide bond formation, translocation, and nascent chain progression. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:91–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
