Determinants of targeting by endogenous and exogenous microRNAs and siRNAs
- PMID: 17872505
- PMCID: PMC2040081
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.768207
Determinants of targeting by endogenous and exogenous microRNAs and siRNAs
Abstract
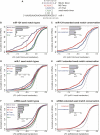
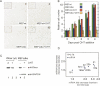
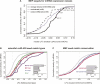
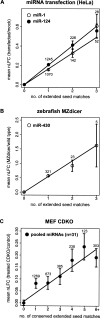
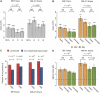
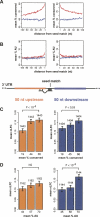
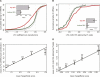
Vertebrate mRNAs are frequently targeted for post-transcriptional repression by microRNAs (miRNAs) through mechanisms involving pairing of 3' UTR seed matches to bases at the 5' end of miRNAs. Through analysis of expression array data following miRNA or siRNA overexpression or inhibition, we found that mRNA fold change increases multiplicatively (i.e., log-additively) with seed match count and that a single 8 mer seed match mediates down-regulation comparable to two 7 mer seed matches. We identified several targeting determinants that enhance seed match-associated mRNA repression, including the presence of adenosine opposite miRNA base 1 and of adenosine or uridine opposite miRNA base 9, independent of complementarity to the siRNA/miRNA. Increased sequence conservation in the approximately 50 bases 5' and 3' of the seed match and increased AU content 3' of the seed match were each independently associated with increased mRNA down-regulation. All of these determinants are enriched in the vicinity of conserved miRNA seed matches, supporting their activity in endogenous miRNA targeting. Together, our results enable improved siRNA off-target prediction, allow integrated ranking of conserved and nonconserved miRNA targets, and show that targeting by endogenous and exogenous miRNAs/siRNAs involves similar or identical determinants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
siRNAs can function as miRNAs.Genes Dev. 2003 Feb 15;17(4):438-42. doi: 10.1101/gad.1064703. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12600936 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 TAR element is processed by Dicer to yield a viral micro-RNA involved in chromatin remodeling of the viral LTR.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Jul 30;8:63. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-63. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17663774 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing.Mol Cell. 2007 Jul 6;27(1):91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.017. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17612493 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer cuts the kidney.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Nov;19(11):2043-6. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008090986. Epub 2008 Oct 15. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18923053 Review. No abstract available.
-
Is the Efficiency of RNA Silencing Evolutionarily Regulated?Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 12;17(5):719. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050719. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27187367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in inner ear biology and pathogenesis.Hear Res. 2012 May;287(1-2):6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Hear Res. 2012. PMID: 22484222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New plasma diagnostic markers for colorectal cancer: transporter fragments of glutamate tRNA origin.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 12;15(5):1299-1313. doi: 10.7150/jca.92102. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38356701 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of microRNA-mRNA Correlations in Tissue Identifies microRNA Targeting Determinants.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Feb 13;9(1):15. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9010015. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 36827548 Free PMC article.
-
Expander: from expression microarrays to networks and functions.Nat Protoc. 2010 Feb;5(2):303-22. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.230. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Nat Protoc. 2010. PMID: 20134430
-
Base-pair conformational switch modulates miR-34a targeting of Sirt1 mRNA.Nature. 2020 Jul;583(7814):139-144. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2336-3. Epub 2020 May 27. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32461691
References
-
- Abbondanzo, S.J., Gadi, I., Stewart, C.L. Derivation of embryonic stem cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:803–823. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bagga, S., Bracht, J., Hunter, S., Massirer, K., Holtz, J., Eachus, R., Pasquinelli, A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
