The Mediator subunit MED1/TRAP220 is required for optimal glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transcription activation
- PMID: 17827210
- PMCID: PMC2094069
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm661
The Mediator subunit MED1/TRAP220 is required for optimal glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transcription activation
Abstract
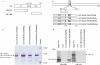
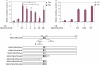
The MED1/TRAP220 subunit of the Mediator plays a key role in facilitating ligand-dependent interactions of this multisubunit coactivator complex with nuclear receptors through their ligand binding domains. The isolated MED1/TRAP220 protein previously was shown to interact with glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in a ligand-dependent manner. However, the functional role of MED1/TRAP220, within the context of the entire Mediator, is not well studied in GR-mediated transcription. In this study, we show that GR binds directly to the Mediator complex and that both LXXLL motifs of MED1/TRAP220 contribute to its binding to GR. Furthermore, using a Med1/Trap220-/- mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) line that lacks entirely MED1/TRAP220, we show that MED1/TRAP220 enhances GR-mediated transcription from an MMTV promoter based-reporter gene and that mutations in the MED1/TRAP220 LXXLL motifs reduce, but do not eliminate, GR-dependent transcription. An analysis of endogenous genes in Med1/Trap220-/- cells has confirmed a variable MED1/TRAP220 requirement for different GR target genes. Taken together, these findings support the idea that Mediator, at least in part through MED1/TRAP220, plays a coregulatory role in ligand-dependent GR-mediated gene expression.
Figures
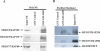


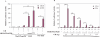
Similar articles
-
Alternative mechanisms by which mediator subunit MED1/TRAP220 regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-stimulated adipogenesis and target gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;28(3):1081-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00967-07. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18039840 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Aurora-A kinase gene expression via GABP recruitment of TRAP220/MED1.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 26;281(21):14691-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600163200. Epub 2006 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16574658
-
MED14 and MED1 differentially regulate target-specific gene activation by the glucocorticoid receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Mar;20(3):560-72. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0318. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16239257
-
How glucocorticoid receptors modulate the activity of other transcription factors: a scope beyond tethering.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Nov 5;380(1-2):41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.12.014. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23267834 Review.
-
Recruitment of chromatin remodelling factors during gene activation via the glucocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):410-4. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961930 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancer RNA Expression in Response to Glucocorticoid Treatment in Murine Macrophages.Cells. 2021 Dec 23;11(1):28. doi: 10.3390/cells11010028. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011590 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity in transcription control at the activation domain-mediator interface.Sci Signal. 2009 May 5;2(69):ra20. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.1164302. Sci Signal. 2009. PMID: 19417216 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional ablation of mediator subunit MED1 (MED1/PPARBP) gene in mouse liver attenuates glucocorticoid receptor agonist dexamethasone-induced hepatic steatosis.Gene Expr. 2009;14(5):291-306. doi: 10.3727/105221609788681213. Gene Expr. 2009. PMID: 19630272 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediator Subunit, Med23 Is Required for Embryonic Survival and Regulation of Canonical WNT Signaling During Cranial Ganglia Development.Front Physiol. 2020 Oct 22;11:531933. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.531933. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33192541 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Fusarium verticillioides Med1 LxxLL Motif Involved in Fumonisin Biosynthesis.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;15(11):652. doi: 10.3390/toxins15110652. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev. 2000;14:121–141. - PubMed
-
- Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. - PubMed
-
- McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O’Malley BW. Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr. Rev. 1999;20:321–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

