A mechanistic basis for converting a receptor tyrosine kinase agonist to an antagonist
- PMID: 17804794
- PMCID: PMC1965485
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0704290104
A mechanistic basis for converting a receptor tyrosine kinase agonist to an antagonist
Abstract
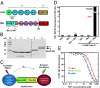
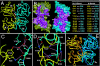
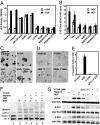
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) activates the Met receptor tyrosine kinase by binding and promoting receptor dimerization. Here we describe a mechanistic basis for designing Met antagonists based on NK1, a natural variant of HGF containing the N-terminal and the first kringle domain. Through detailed biochemical and structural analyses, we demonstrate that both mouse and human NK1 induce Met dimerization via a conserved NK1 dimer interface. Mutations designed to alter the NK1 dimer interface abolish its ability to promote Met dimerization but retain full Met-binding activity. Importantly, these NK1 mutants act as Met antagonists by inhibiting HGF-mediated cell scattering, proliferation, branching, and invasion. The ability to separate the Met-binding activity of NK1 from its Met dimerization activity thus provides a rational basis for designing Met antagonists. This strategy of antagonist design may be applicable for other growth factor receptors by selectively abolishing the receptor activation ability but not the receptor binding of the growth factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
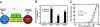

Similar articles
-
Structural basis of MET receptor dimerization by the bacterial invasion protein InlB and the HGF/SF splice variant NK1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.012. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23123275 Review.
-
Crystal structures of NK1-heparin complexes reveal the basis for NK1 activity and enable engineering of potent agonists of the MET receptor.EMBO J. 2001 Oct 15;20(20):5543-55. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5543. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11597998 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin induces dimerization and confers proliferative activity onto the hepatocyte growth factor antagonists NK1 and NK2.J Cell Biol. 1996 May;133(3):709-18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.3.709. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8636243 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for agonism and antagonism of hepatocyte growth factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 27;107(30):13264-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005183107. Epub 2010 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20624990 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into Met receptor activation.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;90(11):972-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.11.014. Epub 2011 Jan 15. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21242015 Review.
Cited by
-
MET: a critical player in tumorigenesis and therapeutic target.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Jul 1;5(7):a009209. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009209. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23818496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting MET in cancer: rationale and progress.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Jan 24;12(2):89-103. doi: 10.1038/nrc3205. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22270953 Review.
-
The angiotensin IV analog Nle-Tyr-Leu-psi-(CH2-NH2)3-4-His-Pro-Phe (norleual) can act as a hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met inhibitor.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Apr;333(1):161-73. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.161711. Epub 2010 Jan 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20086056 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular recognition of parathyroid hormone by its G protein-coupled receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 1;105(13):5034-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801027105. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18375760 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding mutations of HGF are associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss, DFNB39.Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Jul;85(1):25-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jul 2. Am J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19576567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, Vande Woude GF. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Bladt F, Riethmacher D, Isenmann S, Aguzzi A, Birchmeier C. Nature. 1995;376:768–771. - PubMed
-
- Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, Chan AM, Kmiecik TE, Vande Woude GF, Aaronson SA. Science. 1991;251:802–804. - PubMed
-
- Cioce V, Csaky KG, Chan AM, Bottaro DP, Taylor WG, Jensen R, Aaronson SA, Rubin JS. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13110–13115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

