Reactive oxygen species contribute to sleep apnea-induced hypertension in rats
- PMID: 17766485
- PMCID: PMC3792788
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00219.2007
Reactive oxygen species contribute to sleep apnea-induced hypertension in rats
Abstract
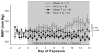
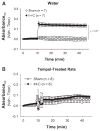
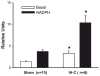
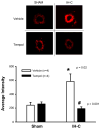
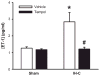
In clinical studies, sleep apnea is associated with hypertension, oxidative stress, and increased circulating endothelin-1 (ET-1). We previously developed a model of sleep apnea by exposing rats to eucapnic intermittent hypoxia (IH-C) during sleep, which increases both blood pressure and plasma levels of ET-1. Because similar protocols in mice increase tissue and plasma markers of oxidative stress, we hypothesized that IH-C generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) contributes to the development of ET-1-dependent hypertension in IH-C rats. To test this, male Sprague-Dawley rats were instrumented with indwelling blood pressure telemeters and drank either plain water or water containing the superoxide dismutase mimetic, Tempol (4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidine-1-oxyl, 1 mM). Mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) were recorded for 3 control days and 14 treatment days with rats exposed 7 h/day to IH-C or air/air cycling (Sham). On day 14, MAP in IH-C rats treated with Tempol (107 +/- 2.29 mmHg) was significantly lower than in untreated IH-C rats (118 +/- 9 mmHg, P < 0.05). Tempol did not affect blood pressure in sham-operated rats (Tempol = 101 +/- 3, water = 101 +/- 2 mmHg). Immunoreactive ET-1 was greater in plasma from IH-C rats compared with plasma from sham-operated rats but was not different from Sham in Tempol-treated IH-C rats. Small mesenteric arteries from IH-C rats but not Tempol-treated IH-C rats had increased superoxide levels as measured by ferric cytochrome c reduction, lucigenin signaling, and dihydroethidium fluorescence. The data show that IH-C increases ET-1 production and vascular ROS levels and that scavenging superoxide prevents both. Thus oxidative stress appears to contribute to increases in ET-1 production and elevated arterial pressure in this rat model of sleep apnea-induced hypertension.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intermittent hypoxia-induced increases in reactive oxygen species activate NFATc3 increasing endothelin-1 vasoconstrictor reactivity.Vascul Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;60(1):17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Vascul Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24239798 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endothelin in intermittent hypoxia-induced hypertension.Hypertension. 2001 Feb;37(2 Pt 2):511-5. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.37.2.511. Hypertension. 2001. PMID: 11230327
-
Augmented endothelin vasoconstriction in intermittent hypoxia-induced hypertension.Hypertension. 2005 Apr;45(4):705-9. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000153794.52852.04. Epub 2005 Feb 28. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 15738350
-
Neural regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors and redox state drives the pathogenesis of hypertension in a rodent model of sleep apnea.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Nov 15;119(10):1152-6. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00162.2015. Epub 2015 May 7. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 25953833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive oxygen radicals and gaseous transmitters in carotid body activation by intermittent hypoxia.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 May;372(2):427-431. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2807-0. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 29470646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin on the expression of hypoxia-induced factor-1α and endothelin-1 in rat carotid body exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Apr;33(2):178-184. doi: 10.1007/s11596-013-1093-z. Epub 2013 Apr 17. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23592126
-
Epigenetic regulation of redox state mediates persistent cardiorespiratory abnormalities after long-term intermittent hypoxia.J Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;595(1):63-77. doi: 10.1113/JP272346. Epub 2016 Oct 2. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27506145 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia augments chemoreflex control of sympathetic activity: role of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2010 Apr 15;171(1):36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2010.02.003. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20153844 Free PMC article.
-
Eucapnic intermittent hypoxia augments endothelin-1 vasoconstriction in rats: role of PKCdelta.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Feb;294(2):H920-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01264.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18083893 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent hypoxia-induced rat pancreatic β-cell apoptosis and protective effects of antioxidant intervention.Nutr Diabetes. 2014 Sep 1;4(9):e131. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2014.28. Nutr Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 25177911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baguet JP, Narkiewicz K, Mallion JM. Update on Hypertension Management: obstructive sleep apnea and hypertension. J Hypertens. 2006;24:205–208. - PubMed
-
- Bao G, Randhawa PM, Fletcher EC. Acute blood pressure elevation during repetitive hypocapnic and eucapnic hypoxia in rats. J Appl Physiol. 1997;82:1071–1078. - PubMed
-
- Boland LL, Shahar E, Iber C, Knopman DS, Kuo TF, Nieto FJ. Measures of cognitive function in persons with varying degrees of sleep-disordered breathing: the Sleep Heart Health Study. J Sleep Res. 2002;11:265–272. - PubMed
-
- Cheng TH, Cheng PY, Shih NL, Chen IB, Wang DL, Chen JJ. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in angiotensin II-induced endothelin-1 gene expression in rat cardiac fibroblasts. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1845–1854. - PubMed
-
- Cheng TH, Shih NL, Chen SY, Loh SH, Cheng PY, Tsai CS, Liu SH, Wang DL, Chen JJ. Reactive oxygen species mediate cyclic strain-induced endothelin-1 gene expression via Ras/Raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33:1805–1814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

