Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin induces phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and Mnk-mediated eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation
- PMID: 17724079
- PMCID: PMC2169067
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00760-07
Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin induces phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and Mnk-mediated eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation
Abstract
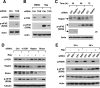
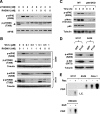
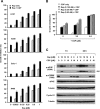
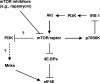
The initiation factor eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) plays a critical role in initiating translation of mRNAs, including those encoding oncogenic proteins. Therefore, eIF4E is considered a survival protein involved in cell cycle progression, cell transformation, and apoptotic resistance. Phosphorylation of eIF4E (usually at Ser209) increases its binding affinity for the cap of mRNA and may also favor its entry into initiation complexes. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors suppress cap-dependent translation through inhibition of the phosphorylation of eIF4E-binding protein 1. Paradoxically, we have shown that inhibition of mTOR signaling increases eIF4E phosphorylation in human cancer cells. In this study, we focused on revealing the mechanism by which mTOR inhibition increases eIF4E phosphorylation. Silencing of either mTOR or raptor could mimic mTOR inhibitors' effects to increase eIF4E phosphorylation. Moreover, knockdown of mTOR, but not rictor or p70S6K, abrogated rapamycin's ability to increase eIF4E phosphorylation. These results indicate that mTOR inhibitor-induced eIF4E phosphorylation is secondary to mTOR/raptor inhibition and independent of p70S6K. Importantly, mTOR inhibitors lost their ability to increase eIF4E phosphorylation only in cells where both Mnk1 and Mnk2 were knocked out, indicating that mTOR inhibitors increase eIF4E phosphorylation through a Mnk-dependent mechanism. Given that mTOR inhibitors failed to increase Mnk and eIF4E phosphorylation in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-deficient cells, we conclude that mTOR inhibition increases eIF4E phosphorylation through a PI3K-dependent and Mnk-mediated mechanism. In addition, we also suggest an effective therapeutic strategy for enhancing mTOR-targeted cancer therapy by cotargeting mTOR signaling and Mnk/eIF4E phosphorylation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of Akt and eIF4E survival pathways by rapamycin-mediated mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition.Cancer Res. 2005 Aug 15;65(16):7052-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0917. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16103051
-
CGP57380 enhances efficacy of RAD001 in non-small cell lung cancer through abrogating mTOR inhibition-induced phosphorylation of eIF4E and activating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):27787-801. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8497. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27050281 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous inhibition of mTOR-containing complex 1 (mTORC1) and MNK induces apoptosis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024849. Epub 2011 Sep 16. PLoS One. 2011. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2020 Sep 10;15(9):e0239102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239102 PMID: 21949767 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Targeting Mnks for cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2012 Feb;3(2):118-31. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.453. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22392765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual abrogation of MNK and mTOR: a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of aggressive cancers.Future Med Chem. 2017 Sep;9(13):1539-1555. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0062. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Future Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28841037 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Survival and Pro-Apoptotic Effects of 6-Shogaol on SW872 Human Liposarcoma Cells via Control of the Intrinsic Caspase Pathway, STAT-3, AMPK, and ER Stress.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 28;10(10):1380. doi: 10.3390/biom10101380. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32998376 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF stimulation of protein synthesis in cortical neurons requires the MAP kinase-interacting kinase MNK1.J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 21;35(3):972-84. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2641-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25609615 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of the novel dual PI3-kinase/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 compared with rapamycin in renal cell carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jul 15;16(14):3628-38. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3022. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20606035 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of p-4EBP1 associates with p-eIF4E and predicts poor prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer patients with resection.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 23;17(6):e0265465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265465. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35737644 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin represses Wnt/β-catenin signaling by binding to TELO2, a regulator of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinases.iScience. 2022 Mar 7;25(3):103912. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103912. eCollection 2022 Mar 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35530256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjornsti, M. A., and P. J. Houghton. 2004. Lost in translation: dysregulation of cap-dependent translation and cancer. Cancer Cell 5: 519-523. - PubMed
-
- Bjornsti, M. A., and P. J. Houghton. 2004. The TOR pathway: a target for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4: 335-348. - PubMed
-
- De Benedetti, A., and A. L. Harris. 1999. eIF4E expression in tumors: its possible role in progression of malignancies. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 31: 59-72. - PubMed
-
- Franch, H. A., X. Wang, S. Sooparb, N. S. Brown, and J. Du. 2002. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is required for epidermal growth factor to suppress proteolysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13: 903-909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
