Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential
- PMID: 17717971
- PMCID: PMC2426795
Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential
Abstract
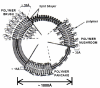
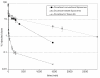
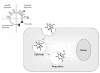
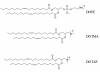
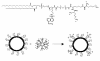
Among several promising new drug-delivery systems, liposomes represent an advanced technology to deliver active molecules to the site of action, and at present several formulations are in clinical use. Research on liposome technology has progressed from conventional vesicles ("first-generation liposomes") to "second-generation liposomes", in which long-circulating liposomes are obtained by modulating the lipid composition, size, and charge of the vesicle. Liposomes with modified surfaces have also been developed using several molecules, such as glycolipids or sialic acid. A significant step in the development of long-circulating liposomes came with inclusion of the synthetic polymer poly-(ethylene glycol) (PEG) in liposome composition. The presence of PEG on the surface of the liposomal carrier has been shown to extend blood-circulation time while reducing mononuclear phagocyte system uptake (stealth liposomes). This technology has resulted in a large number of liposome formulations encapsulating active molecules, with high target efficiency and activity. Further, by synthetic modification of the terminal PEG molecule, stealth liposomes can be actively targeted with monoclonal antibodies or ligands. This review focuses on stealth technology and summarizes pre-clinical and clinical data relating to the principal liposome formulations; it also discusses emerging trends of this promising technology.
Figures
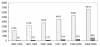

Similar articles
-
Liposomal drug delivery systems: an update review.Curr Drug Deliv. 2007 Oct;4(4):297-305. doi: 10.2174/156720107782151269. Curr Drug Deliv. 2007. PMID: 17979650 Review.
-
Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013 Feb 22;8(1):102. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-8-102. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013. PMID: 23432972 Free PMC article.
-
Stealth liposomes: an improved sustained release system for 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine.Cancer Res. 1992 May 1;52(9):2431-9. Cancer Res. 1992. PMID: 1568213
-
Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Jan;65(1):36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.037. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23036225 Review.
-
From conventional to stealth liposomes: a new frontier in cancer chemotherapy.Tumori. 2003 May-Jun;89(3):237-49. doi: 10.1177/030089160308900302. Tumori. 2003. PMID: 12908776 Review.
Cited by
-
Light-triggered switching of liposome surface charge directs delivery of membrane impermeable payloads in vivo.Nat Commun. 2020 Jul 20;11(1):3638. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17360-9. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32686667 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoliposome-based targeted delivery of the CRISPR/Cas9gRNA-IL30 complex inhibits prostate cancer and prolongs survival.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Sep;56(9):2033-2051. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01310-2. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39232121 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic RGD peptide-modified liposomal drug delivery system: enhanced cellular uptake in vitro and improved pharmacokinetics in rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3803-11. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S33541. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22888235 Free PMC article.
-
Transferrin-Functionalized Liposomes for the Delivery of Gallic Acid: A Therapeutic Approach for Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 11;14(10):2163. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102163. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297599 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic synthesis of PEG- and folate-conjugated liposomes for one-step formation of targeted stealth nanocarriers.Pharm Res. 2013 Jun;30(6):1597-607. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-0998-3. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23386106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams GP, Weiner LM. Monoclonal antibody therapy of cancer. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1147–57. - PubMed
-
- Adlakha-Hutcheon G, Bally MB, Shew CR, et al. Controlled destabilization of a liposomal drug delivery system enhances mitoxantrone antitumor activity. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17:775–9. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal AK, Gupta CM. Tuftsin-bearing liposomes in treatment of macrophage-based infections. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2000;41:135–46. - PubMed
-
- Alberts DS, Muggia FM, Carmichael J, et al. Efficacy and safety of liposomal anthracyclines in phase I/II clinical trials. Semin Oncol. 2004;31(Suppl 13):53–90. - PubMed
-
- Allen C, Dos SN, Gallagher R, et al. Controlling the physical behavior and biological performance of liposome formulations through use of surface grafted poly(ethylene glycol) Biosc Rep. 2002;22:225–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
