Protein kinase A and Sch9 cooperatively regulate induction of autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 17699586
- PMCID: PMC1995722
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0485
Protein kinase A and Sch9 cooperatively regulate induction of autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
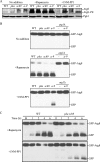
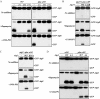
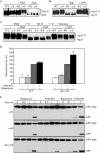
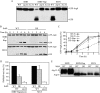
Autophagy is a highly conserved, degradative process in eukaryotic cells. The rapamycin-sensitive Tor kinase complex 1 (TORC1) has a major role in regulating induction of autophagy; however, the regulatory mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, we find that the protein kinase A (PKA) and Sch9 signaling pathways regulate autophagy cooperatively in yeast. Autophagy is induced in cells when PKA and Sch9 are simultaneously inactivated. Mutant alleles of these kinases bearing a mutation that confers sensitivity to the ATP-analogue inhibitor C3-1'-naphthyl-methyl PP1 revealed that autophagy was induced independently of effects on Tor kinase. The PKA-Sch9-mediated autophagy depends on the autophagy-related 1 kinase complex, which is also essential for TORC1-regulated autophagy, the transcription factors Msn2/4, and the Rim15 kinase. The present results suggest that autophagy is controlled by the signals from at least three partly separate nutrient-sensing pathways that include PKA, Sch9, and TORC1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rim15 and Sch9 kinases are involved in induction of autophagic degradation of ribosomes in budding yeast.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017 Feb;81(2):307-310. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2016.1234928. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27659307
-
TOR and PKA signaling pathways converge on the protein kinase Rim15 to control entry into G0.Mol Cell. 2003 Dec;12(6):1607-13. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00485-4. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14690612
-
Life span extension by calorie restriction depends on Rim15 and transcription factors downstream of Ras/PKA, Tor, and Sch9.PLoS Genet. 2008 Jan;4(1):e13. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0040013. Epub 2007 Dec 13. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18225956 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of TOR and PKA Signaling in S. cerevisiae.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 26;12(2):210. doi: 10.3390/biom12020210. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TORC1-Sch9 pathway as a crucial mediator of chronological lifespan in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEMS Yeast Res. 2018 Aug 1;18(5). doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foy048. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018. PMID: 29788208 Review.
Cited by
-
Ksp1 kinase regulates autophagy via the target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) pathway.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 11;287(20):16300-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344952. Epub 2012 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22447937 Free PMC article.
-
The Aspergillus nidulans ATM kinase regulates mitochondrial function, glucose uptake and the carbon starvation response.G3 (Bethesda). 2014 Jan 10;4(1):49-62. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.008607. G3 (Bethesda). 2014. PMID: 24192833 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose regulates clathrin adaptors at the trans-Golgi network and endosomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Oct;22(19):3671-83. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0309. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21832155 Free PMC article.
-
Sch9 regulates ribosome biogenesis via Stb3, Dot6 and Tod6 and the histone deacetylase complex RPD3L.EMBO J. 2011 Jul 5;30(15):3052-64. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.221. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21730963 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Regulation of Autophagy and Its Role in Neuronal Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;52(3):1190-1209. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8921-4. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25316381 Review.
References
-
- Beck T., Hall M. N. The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature. 1999;402:689–692. - PubMed
-
- Chen J. C., Powers T. Coordinate regulation of multiple and distinct biosynthetic pathways by TOR and PKA kinases in S. cerevisiae. Curr. Genet. 2006;49:281–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

