Sox9 regulates cell proliferation and is required for Paneth cell differentiation in the intestinal epithelium
- PMID: 17698607
- PMCID: PMC2064470
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200704152
Sox9 regulates cell proliferation and is required for Paneth cell differentiation in the intestinal epithelium
Abstract
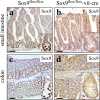
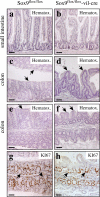
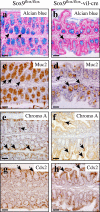
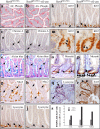
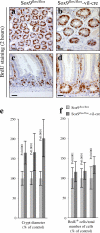
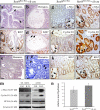
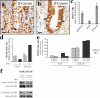
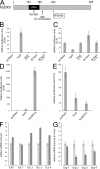
The HMG-box transcription factor Sox9 is expressed in the intestinal epithelium, specifically, in stem/progenitor cells and in Paneth cells. Sox9 expression requires an active beta-catenin-Tcf complex, the transcriptional effector of the Wnt pathway. This pathway is critical for numerous aspects of the intestinal epithelium physiopathology, but processes that specify the cell response to such multipotential signals still remain to be identified. We inactivated the Sox9 gene in the intestinal epithelium to analyze its physiological function. Sox9 inactivation affected differentiation throughout the intestinal epithelium, with a disappearance of Paneth cells and a decrease of the goblet cell lineage. Additionally, the morphology of the colon epithelium was severely altered. We detected general hyperplasia and local crypt dysplasia in the intestine, and Wnt pathway target genes were up-regulated. These results highlight the central position of Sox9 as both a transcriptional target and a regulator of the Wnt pathway in the regulation of intestinal epithelium homeostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SOX9 is required for the differentiation of paneth cells in the intestinal epithelium.Gastroenterology. 2007 Aug;133(2):539-46. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.020. Epub 2007 May 21. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17681175
-
SOX9 is an intestine crypt transcription factor, is regulated by the Wnt pathway, and represses the CDX2 and MUC2 genes.J Cell Biol. 2004 Jul 5;166(1):37-47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200311021. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15240568 Free PMC article.
-
Sox9 induction, ectopic Paneth cells, and mitotic spindle axis defects in mouse colon adenomatous epithelium arising from conditional biallelic Apc inactivation.Am J Pathol. 2013 Aug;183(2):493-503. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.04.013. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23769888 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SOX9 transcription factor in pancreatic and duodenal development.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Nov 15;22(22):2935-43. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0106. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23806070 Review.
-
The Yin-Yang of TCF/beta-catenin signaling.Adv Cancer Res. 2000;77:1-24. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60783-6. Adv Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10549354 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic Features in Histologically Normal Mucosa: Novel Insights Into Field Effect From a Mega-Analysis of Colorectal Transcriptomes.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul;11(7):e00210. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000210. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32764205 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling, stem cells, and cancer of the gastrointestinal tract.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Apr 1;4(4):a007989. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007989. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22474007 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal redox biology and oxidative stress.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012 Sep;23(7):729-37. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.03.014. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22484611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification, visualization and clonal analysis of intestinal stem cells in fish.Development. 2016 Oct 1;143(19):3470-3480. doi: 10.1242/dev.134098. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Development. 2016. PMID: 27578784 Free PMC article.
-
Acute stress disrupts intestinal homeostasis via GDNF-RET.Cell Prolif. 2020 Oct;53(10):e12889. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12889. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32808420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afonja, O., B.M. Raaka, A. Huang, S. Das, X. Zhao, E. Helmer, D. Juste, and H.H. Samuels. 2002. RAR agonists stimulate SOX9 gene expression in breast cancer cell lines: evidence for a role in retinoid-mediated growth inhibition. Oncogene. 21:7850–7860. - PubMed
-
- Andreu, P., S. Colnot, C. Godard, S. Gad, P. Chafey, M. Niwa-Kawakita, P. Laurent-Puig, A. Kahn, S. Robine, C. Perret, and B. Romagnolo. 2005. Crypt-restricted proliferation and commitment to the Paneth cell lineage following Apc loss in the mouse intestine. Development. 132:1443–1451. - PubMed
-
- Batlle, E., J.T. Henderson, H. Beghtel, M.M.W. van den Born, E. Sancho, G. Huls, J. Meeldijk, J. Robertson, M. van de Wetering, T. Pawson, and H. Clevers. 2002. β-Catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/EphrinB. Cell. 111:251–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

