The control of phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate concentrations by activation of the Src homology 2 domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 2, SHIP2
- PMID: 17672824
- PMCID: PMC2049017
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070558
The control of phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate concentrations by activation of the Src homology 2 domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 2, SHIP2
Abstract
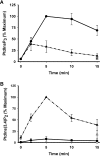
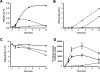
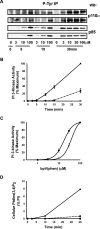
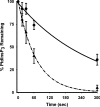
Activation of class Ia PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) produces PtdInsP3, a vital intracellular mediator whose degradation generates additional lipid signals. In the present study vanadate analogues that inhibit PTPs (protein tyrosine phosphatases) were used to probe the mechanisms which regulate the concentrations of these molecules allowing their independent or integrated function. In 1321N1 cells, which lack PtdInsP3 3-phosphatase activity, sodium vanadate or a cell permeable derivative, bpV(phen) [potassium bisperoxo(1,10-phenanthroline)oxovanadate (V)], increased the recruitment into anti-phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitates of PI3K activity and of the p85 and p110a subunits of class Ia PI3K and enhanced the recruitment of PI3K activity stimulated by PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor). However, neither inhibitor much increased cellular PtdInsP3 concentrations, but both diminished dramatically the accumulation of PtdInsP3 stimulated by PDGF or insulin and markedly increased the control and stimulated concentrations of PtdIns(3,4)P2. These actions were accounted for by the ability of PTP inhibitors to stimulate the activity of endogenous PtdInsP3 5-phosphatase(s), particularly SHIP2 (Src homology 2 domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 2) and to inhibit types I and II PtdIns(3,4)P2 4-phosphatases. Thus bpV(phen) promoted the translocation of SHIP2 from the cytosol to a Triton X-100-insoluble fraction and induced a marked (5-10-fold) increase in SHIP2 specific activity mediated by enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation. The net effect of these inhibitors was, therefore, to switch the signal output of class I PI3K from PtdInsP3 to PtdIns(3,4)P2. A key component controlling this shift in the balance of lipid signals is the activation of SHIP2 by increased tyrosine phosphorylation, an effect observed in HeLa cells in response to both PTP inhibitors and epidermal growth factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dual role of SRC homology domain 2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 in the regulation of platelet-derived growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I signaling in rat vascular smooth muscle cells.Endocrinology. 2003 Sep;144(9):4204-14. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0190. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12933696
-
Regulation of PDGF-stimulated SHIP2 tyrosine phosphorylation and association with Shc in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jun;211(3):598-607. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20965. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17219406
-
Characterization of VPS34-IN1, a selective inhibitor of Vps34, reveals that the phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate-binding SGK3 protein kinase is a downstream target of class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase.Biochem J. 2014 Nov 1;463(3):413-27. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140889. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25177796 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN and Other PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 Lipid Phosphatases in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 2;21(23):9189. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239189. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33276499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SH2 domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase-2: SHIP2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;37(11):2260-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.05.003. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964236 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoinositides: tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation.Physiol Rev. 2013 Jul;93(3):1019-137. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00028.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23899561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross talk between the Akt and p38α pathways in macrophages downstream of Toll-like receptor signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Nov;33(21):4152-65. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01691-12. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23979601 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase (SHIP1) by the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 24;284(30):20070-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.016865. Epub 2009 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19494109 Free PMC article.
-
Endophilin marks and controls a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway.Nature. 2015 Jan 22;517(7535):460-5. doi: 10.1038/nature14067. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25517094
-
SHIP2 (SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase 2) SH2 domain negatively controls SHIP2 monoubiquitination in response to epidermal growth factor.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 25;284(52):36062-36076. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.064923. Epub 2009 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19880507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- Vanhaesebroeck B., Leevers S. J., Ahmadi K., Timms J., Katso R., Driscoll P. C., Woscholski R., Parker P. J., Waterfield M. D. Synthesis and function of 3-phosphorylated inositol lipids. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:535–602. - PubMed
-
- Lemmon M. A. Phosphoinositide recognition domains. Traffic. 2003;4:201–213. - PubMed
-
- Di Paolo G., De Camilli P. Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature. 2006;443:651–657. - PubMed
-
- Leslie N. R., Downes C. P. PTEN: the down side of PI 3-kinase signalling. Cell. Signalling. 2002;14:285–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

