3D analysis of founder cell and fusion competent myoblast arrangements outlines a new model of myoblast fusion
- PMID: 17662708
- PMCID: PMC2709992
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.06.024
3D analysis of founder cell and fusion competent myoblast arrangements outlines a new model of myoblast fusion
Abstract
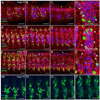
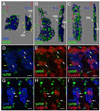
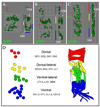
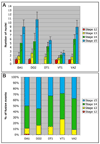
Formation of the Drosophila larval body wall muscles requires the specification, coordinated cellular behaviors and fusion of two cell types: Founder Cells (FCs) that control the identity of the individual muscle and Fusion Competent Myoblasts (FCMs) that provide mass. These two cell types come together to control the final size, shape and attachment of individual muscles. However, the spatial arrangement of these cells over time, the sequence of fusion events and the contribution of these cellular relationships to the fusion process have not been addressed. We analyzed the three-dimensional arrangements of FCs and FCMs over the course of myoblast fusion and assayed whether these issues impact the process of myoblast fusion. We examined the timing of the fusion process by analyzing the fusion profile of individual muscles in wild type and fusion mutants. We showed that there are two temporal phases of myoblast fusion in wild type embryos. Limited fusion events occur during the first 3 h of fusion, while the majority of fusion events occur in the remaining 2.5 h. Altogether, our data have led us to propose a new model of myoblast fusion where the frequency of myoblast fusion events may be influenced by the spatial arrangements of FCs and FCMs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Myoblast fusion in Drosophila.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Nov 1;316(18):3007-13. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.05.018. Epub 2010 May 24. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20580706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and functional analysis of a novel Fusion Competent Myoblast specific GAL4 driver.Gene Expr Patterns. 2008 Jan;8(2):87-91. doi: 10.1016/j.modgep.2007.10.002. Epub 2007 Oct 13. Gene Expr Patterns. 2008. PMID: 17988956 Free PMC article.
-
Mind bomb 2, a founder myoblast-specific protein, regulates myoblast fusion and muscle stability.Development. 2008 Mar;135(5):849-57. doi: 10.1242/dev.015529. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Development. 2008. PMID: 18216171
-
Identification of singles bar as a direct transcriptional target of Drosophila Myocyte enhancer factor-2 and a regulator of adult myoblast fusion.Dev Biol. 2015 May 15;401(2):299-309. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.02.026. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25797154 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Myoblast Fusion: Invasion and Resistance for the Ultimate Union.Annu Rev Genet. 2019 Dec 3;53:67-91. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120116-024603. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Annu Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 31283358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dock mediates Scar- and WASp-dependent actin polymerization through interaction with cell adhesion molecules in founder cells and fusion-competent myoblasts.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jan 1;126(Pt 1):360-72. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113860. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 22992459 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoskeletal remodeling during myotube assembly and guidance: coordinating the actin and microtubule networks.Commun Integr Biol. 2009 Sep;2(5):452-7. doi: 10.4161/cib.2.5.9158. Commun Integr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19907716 Free PMC article.
-
Myoblast fusion: when it takes more to make one.Dev Biol. 2010 May 1;341(1):66-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.10.024. Epub 2009 Nov 20. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19932206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invasive podosomes and myoblast fusion.Curr Top Membr. 2011;68:235-58. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385891-7.00010-6. Curr Top Membr. 2011. PMID: 21771502 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
An invasive podosome-like structure promotes fusion pore formation during myoblast fusion.J Cell Biol. 2010 Nov 29;191(5):1013-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201006006. Epub 2010 Nov 22. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21098115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abmayr SM, Kocherlakota KS. Muscle Morphogenesis: The Process of Embryonic Myoblast Fusion. In: Sink H, editor. Muscle Development in Drosophila. New York: Springer Science + Business Media, Inc.; 2006.
-
- Artero R, Furlong EE, Beckett K, Scott MP, Baylies M. Notch and Ras signaling pathway effector genes expressed in fusion competent and founder cells during Drosophila myogenesis. Development. 2003;130:6257–6272. - PubMed
-
- Artero RD, Castanon I, Baylies MK. The immunoglobulin-like protein Hibris functions as a dose-dependent regulator of myoblast fusion and is differentially controlled by Ras and Notch signaling. Development. 2001;128:4251–4264. - PubMed
-
- Bate M. The embryonic development of larval muscles in Drosophila. Development. 1990;110:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Bate M. The mesoderm and its derivatives. In: MMA Bate A, editor. The Development of Drosophila melanogaster. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 GM056989-04/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM078318/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM 586989/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056989-05/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056989-06A2/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056989-07/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM78318/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056989-01A1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM078318-01A1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056989-03/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056989-02/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056989/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM078318-02/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

