Plasminogen activation induced pericellular fibronectin proteolysis promotes fibroblast apoptosis
- PMID: 17656680
- PMCID: PMC2176129
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0174OC
Plasminogen activation induced pericellular fibronectin proteolysis promotes fibroblast apoptosis
Abstract
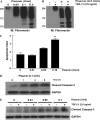
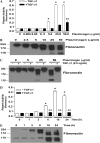
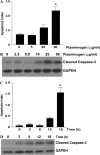
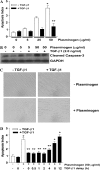
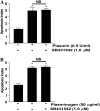
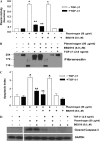
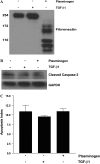
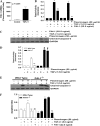
Apoptosis of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts is a critical event in the resolution of tissue repair responses; however, mechanisms for the regulation of (myo)fibroblast apoptosis/survival remain unclear. In this study, we demonstrate counter-regulatory interactions between the plasminogen activation system and transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) in the control of fibroblast apoptosis. Plasmin treatment induced fibroblast apoptosis in a time- and dose-dependent manner in association with proteolytic degradation of extracellular matrix proteins, as detected by the release of soluble fibronectin peptides. Plasminogen, which was activated to plasmin by fibroblasts, also induced fibronectin proteolysis and fibroblast apoptosis, both of which were blocked by alpha2-antiplasmin but not by inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase activity. TGF-beta1 protected fibroblasts from apoptosis induced by plasminogen but not from apoptosis induced by exogenous plasmin. The protection from plasminogen-induced apoptosis conferred by TGF-beta1 is associated with the up-regulation of plasminogen activator-1 (PAI-1) expression and inhibition of plasminogen activation. Moreover, lung fibroblasts from mice genetically deficient in PAI-1 lose the protective effect of TGF-beta1 against plasminogen-induced apoptosis. These findings support a novel role for the plasminogen activation system in the regulation of fibroblast apoptosis and a potential role of TGF-beta1/PAI-1 in promoting (myo)fibroblast survival in chronic fibrotic disorders.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TGF-β1 Suppresses Plasmin and MMP Activity in Flexor Tendon Cells via PAI-1: Implications for Scarless Flexor Tendon Repair.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Feb;230(2):318-26. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24707. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 24962629 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic value of small molecule inhibitor to plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 for lung fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Jan;46(1):87-95. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0139OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21852684 Free PMC article.
-
Positive feedback loop between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and transforming growth factor-beta1 during renal fibrosis in diabetes.Am J Nephrol. 2009;30(6):481-90. doi: 10.1159/000242477. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Am J Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19786738
-
The TGF-β1/p53/PAI-1 Signaling Axis in Vascular Senescence: Role of Caveolin-1.Biomolecules. 2019 Aug 3;9(8):341. doi: 10.3390/biom9080341. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31382626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular biomarkers of Graves' ophthalmopathy.Exp Mol Pathol. 2019 Feb;106:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.11.004. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30414981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress and Lung Fibrosis: Towards an Adverse Outcome Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 6;24(15):12490. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512490. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast Differentiation and Matrix Remodeling Impaired under Simulated Microgravity in 3D Cell Culture Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 2;22(21):11911. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111911. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769342 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Lung Fibroblast Resistance to Fas-Mediated Apoptosis Is Dependent on the Baculoviral Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein 4 and the Cellular FLICE-Inhibitory Protein.Front Physiol. 2017 Mar 14;8:128. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00128. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28352235 Free PMC article.
-
p53 and Myofibroblast Apoptosis in Organ Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 4;24(7):6737. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076737. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAI-1 inhibition by simvastatin as a positive adjuvant in cell therapy.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):1511-1517. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4562-4. Epub 2019 Jan 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30612281 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

