The mouse homolog of HEN1 is a potential methylase for Piwi-interacting RNAs
- PMID: 17652135
- PMCID: PMC1950760
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.659307
The mouse homolog of HEN1 is a potential methylase for Piwi-interacting RNAs
Abstract
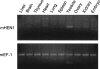
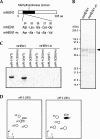
Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are a novel class of small regulatory RNAs that are expressed specifically and abundantly in germ cells. Mammalian piRNAs are 26-31 nucleotides in length and bind to Piwi proteins, but their function and biogenesis remain elusive. We previously showed that mammalian piRNAs are 2'-O-methylated at their 3' termini. The biosynthetic mechanism and function of this modification is unknown. Here, we report that the mouse homolog (mHEN1) of HEN1, a plant microRNA (miRNA) 2'-O-methyltransferase, is expressed specifically in testis and methylates 3' termini of piRNAs in vitro. These findings provide insight into the biogenesis of piRNAs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
2'-O-methyl modification in mouse piRNAs and its methylase.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2007;(51):417-8. doi: 10.1093/nass/nrm209. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2007. PMID: 18029764
-
Pimet, the Drosophila homolog of HEN1, mediates 2'-O-methylation of Piwi- interacting RNAs at their 3' ends.Genes Dev. 2007 Jul 1;21(13):1603-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.1563607. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17606638 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Piwi-interacting RNAs are 2'-O-methylated at their 3' termini.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Apr;14(4):347-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1218. Epub 2007 Mar 25. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17384647
-
Small RNAs just got bigger: Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) in mammalian testes.Genes Dev. 2006 Aug 1;20(15):1993-7. doi: 10.1101/gad.1456106. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16882976 Review.
-
Regulation of small RNA stability: methylation and beyond.Cell Res. 2012 Apr;22(4):624-36. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.36. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22410795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mili and Miwi target RNA repertoire reveals piRNA biogenesis and function of Miwi in spermiogenesis.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Aug;19(8):773-81. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2347. Epub 2012 Jul 29. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22842725 Free PMC article.
-
The burgeoning importance of PIWI-interacting RNAs in cancer progression.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Apr;67(4):653-662. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2491-7. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38198029 Review.
-
PNLDC1 catalysis and postnatal germline function are required for piRNA trimming, LINE1 silencing, and spermatogenesis in mice.PLoS Genet. 2024 Sep 23;20(9):e1011429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011429. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39312580 Free PMC article.
-
Argonautes confront new small RNAs.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007 Oct;11(5):569-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.08.032. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007. PMID: 17928262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the Trypanosoma brucei HEN1 family methyltransferase in small interfering RNA modification.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Jan;13(1):77-86. doi: 10.1128/EC.00233-13. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 24186950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravin, A.A., Lagos-Quintana, M., Yalcin, A., Zavolan, M., Marks, D., Snyder, B., Gaasterland, T., Meyer, J., Tuschl, T. The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev. Cell. 2003;5:337–350. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Brennecke, J., Aravin, A.A., Stark, A., Dus, M., Kellis, M., Sachidanandam, R., Hannon, G.J. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila . Cell. 2007;128:1089–1103. - PubMed
-
- Carmell, M.A., Xuan, Z., Zhang, M.Q., Hannon, G.J. The Argonaute family: Tentacles that reach into RNAi, developmental control, stem cell maintenance, and tumorigenesis. Genes & Dev. 2002;16:2733–2742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
