Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA
- PMID: 17641203
- PMCID: PMC4283197
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1140956
Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA
Abstract
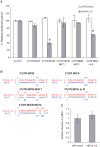
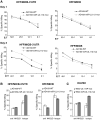
Virally encoded microRNAs (miRNAs) have recently been discovered in herpesviruses. However, their biological roles are mostly unknown. We developed an algorithm for the prediction of miRNA targets and applied it to human cytomegalovirus miRNAs, resulting in the identification of the major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain B (MICB) gene as a top candidate target of hcmv-miR-UL112. MICB is a stress-induced ligand of the natural killer (NK) cell activating receptor NKG2D and is critical for the NK cell killing of virus-infected cells and tumor cells. We show that hcmv-miR-UL112 specifically down-regulates MICB expression during viral infection, leading to decreased binding of NKG2D and reduced killing by NK cells. Our results reveal a miRNA-based immunoevasion mechanism that appears to be exploited by human cytomegalovirus.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immunology. Outwitted by viral RNAs.Science. 2007 Jul 20;317(5836):329-30. doi: 10.1126/science.1146077. Science. 2007. PMID: 17641188 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein UL16 causes intracellular sequestration of NKG2D ligands, protecting against natural killer cell cytotoxicity.J Exp Med. 2003 Jun 2;197(11):1427-39. doi: 10.1084/jem.20022059. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12782710 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of human cytomegalovirus infection on ligands for the activating NKG2D receptor of NK cells: up-regulation of UL16-binding protein (ULBP)1 and ULBP2 is counteracted by the viral UL16 protein.J Immunol. 2003 Jul 15;171(2):902-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.2.902. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12847260
-
Intracellular retention of the MHC class I-related chain B ligand of NKG2D by the human cytomegalovirus UL16 glycoprotein.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 15;170(8):4196-200. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.8.4196. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12682252
-
The UL16-binding proteins, a novel family of MHC class I-related ligands for NKG2D, activate natural killer cell functions.Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:185-92. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810115.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513139 Review.
-
Battle of the midgets: innate microRNA networking.RNA Biol. 2012 Jun;9(6):792-8. doi: 10.4161/rna.19717. Epub 2012 May 23. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22617882 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune evasion by proteolytic shedding of natural killer group 2, member D ligands in Helicobacter pylori infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1282680. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1282680. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318189 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-based mechanisms regulating host-virus interactions.Immunol Rev. 2013 May;253(1):97-111. doi: 10.1111/imr.12053. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23550641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral miRNA regulation of host gene expression.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 15;146:2-19. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36463091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways.Viruses. 2020 Jul 10;12(7):746. doi: 10.3390/v12070746. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32664401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA-mediated control of HLA-G expression and function.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033395. Epub 2012 Mar 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22438923 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

