Activation of interleukin-1 signaling cascades in normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage
- PMID: 17640966
- PMCID: PMC1959501
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.061083
Activation of interleukin-1 signaling cascades in normal and osteoarthritic articular cartilage
Abstract
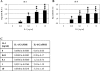
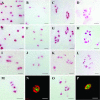
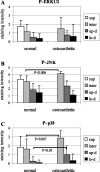
Interleukin (IL)-1 is one of the most important catabolic cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. In this study, we were interested in whether we could identify IL-1 expression and activity within normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. mRNA expression of IL-1beta and of one of its major target genes, IL-6, was observed at very low levels in normal cartilage, whereas only a minor up-regulation of these cytokines was noted in osteoarthritic cartilage, suggesting that IL-1 signaling is not a major event in osteoarthritis. However, immunolocalization of central mediators involved in IL-1 signaling pathways [38-kd protein kinases, phospho (P)-38-kd protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, P-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 1/2, P-c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 1/2, and nuclear factor kappaB] showed that the four IL-1 signaling cascades are functional in normal and osteoarthritic articular chondrocytes. In vivo, we found that IL-1 expression and signaling mechanisms were detectible in the upper zones of normal cartilage, whereas these observations were more pronounced in the upper portions of osteoarthritic cartilage. Given these expression and distribution patterns, our data support two roles for IL-1 in the pathophysiology of articular cartilage. First, chondrocytes in the upper zone of osteoarthritic articular cartilage seem to activate catabolic signaling pathways that may be in response to diffusion of external IL-1 from the synovial fluid. Second, IL-1 seems to be involved in normal cartilage tissue homeostasis as shown by identification of baseline expression patterns and signaling cascade activation.
Figures
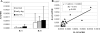


Similar articles
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma1 expression is diminished in human osteoarthritic cartilage and is downregulated by interleukin-1beta in articular chondrocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(2):R31. doi: 10.1186/ar2151. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17386086 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1beta induction of IL-6 and LIF in normal articular human chondrocytes involves the ERK, p38 and NFkappaB signaling pathways.Cytokine. 2004 Oct 7;28(1):17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2004.06.003. Cytokine. 2004. PMID: 15341921
-
Bone morphogenetic protein and transforming growth factor beta inhibitory Smads 6 and 7 are expressed in human adult normal and osteoarthritic cartilage in vivo and are differentially regulated in vitro by interleukin-1beta.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Nov;50(11):3535-40. doi: 10.1002/art.20750. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15529348
-
Regulation of senescence associated signaling mechanisms in chondrocytes for cartilage tissue regeneration.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016 Feb;24(2):196-205. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.07.008. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016. PMID: 26190795 Review.
-
NF-kappaB as a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006 Sep;14(9):839-48. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2006.04.008. Epub 2006 May 26. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006. PMID: 16730463 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin 1β and lipopolysaccharides induction dictate chondrocyte morphological properties and reduce cellular roughness and adhesion energy comparatively.Biointerphases. 2022 Sep 30;17(5):051001. doi: 10.1116/6.0001986. Biointerphases. 2022. PMID: 36180273 Free PMC article.
-
Muscone protects vertebral end-plate degeneration by antiinflammatory property.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010 Jun;468(6):1600-10. doi: 10.1007/s11999-009-1079-0. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010. PMID: 19763723 Free PMC article.
-
Ozone induces autophagy by activating PPARγ/mTOR in rat chondrocytes treated with IL-1β.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Jul 16;17(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03233-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35842709 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA Related to the Chondrocyte ECM Regulates MMP13 Expression by Functioning as a MiR-136 'Sponge' in Human Cartilage Degradation.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 2;6:22572. doi: 10.1038/srep22572. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26931159 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors in Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis.Biology (Basel). 2020 Sep 14;9(9):290. doi: 10.3390/biology9090290. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32937960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goldring MB. Osteoarthritis and cartilage: the role of cytokines. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2000;2:459–465. - PubMed
-
- Goldring MB. The role of cytokines as inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis: lessons from animal models. Connect Tissue Res. 1999;40:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Arend WP, Dayer J-M. Inhibition of the production and affects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor α in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:151–160. - PubMed
-
- Westacott CI, Sharif M. Cytokines in osteoarthritis: mediators or markers of joint destruction? Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996;25:254–272. - PubMed
-
- Tetlow LC, Adlam DJ, Woolley DE. Matrix metalloproteinase and proinflammatory cytokine production by chondrocytes of human osteoarthritic cartilage: associations with degenerative changes. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:585–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

