GDI-1 phosphorylation switch at serine 96 induces RhoA activation and increased endothelial permeability
- PMID: 17636025
- PMCID: PMC2099605
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00523-07
GDI-1 phosphorylation switch at serine 96 induces RhoA activation and increased endothelial permeability
Abstract
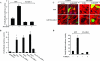
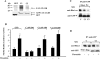
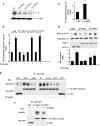
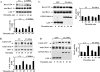
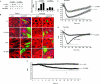
We identified the GDI-1-regulated mechanism of RhoA activation from the Rho-GDI-1 complex and its role in mediating increased endothelial permeability. Thrombin stimulation failed to induce RhoA activation and actin stress fiber formation in human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells transduced with full-length GDI-1. Expression of a GDI-1 mutant form (C-GDI) containing the C terminus (aa 69 to 204) also prevented RhoA activation, whereas further deletions failed to alter RhoA activation. We observed that protein kinase Calpha-mediated phosphorylation of the C terminus of GDI-1 at Ser96 reduced the affinity of GDI-1 for RhoA and thereby enabled RhoA activation. Rendering GDI-1 phosphodefective with a Ser96 --> Ala substitution rescued the inhibitory activity of GDI-1 toward RhoA but did not alter the thrombin-induced activation of other Rho GTPases, i.e., Rac1 and Cdc42. Phosphodefective mutant GDI-1 also suppressed myosin light chain phosphorylation, actin stress fiber formation, and the increased endothelial permeability induced by thrombin. In contrast, expressing the phospho-mimicking mutant S96D-GDI-1 protein induced RhoA activity and increased endothelial permeability independently of thrombin stimulation. These results demonstrate the crucial role of the phosphorylation of the C terminus of GDI-1 at S96 in selectively activating RhoA. Inhibiting GDI-1 phosphorylation at S96 is a potential therapeutic target for modulating RhoA activity and thus preventing the increase in endothelial permeability associated with vascular inflammation.
Figures
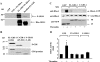
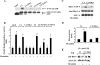
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C-alpha signals rho-guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor phosphorylation and rho activation and regulates the endothelial cell barrier function.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 22;276(25):22614-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101927200. Epub 2001 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11309397
-
Activation of RhoA by thrombin in endothelial hyperpermeability: role of Rho kinase and protein tyrosine kinases.Circ Res. 2000 Aug 18;87(4):335-40. doi: 10.1161/01.res.87.4.335. Circ Res. 2000. PMID: 10948069
-
Phosphorylation of GTP dissociation inhibitor by PKA negatively regulates RhoA.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Nov;295(5):C1161-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00139.2008. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18768928 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of RhoA GTPase and various transcription factors in the RhoA pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):6381-6392. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26487. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29377108 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial cell activation and permeability responses to thrombin.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1995 Oct;6(7):609-26. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199510000-00001. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1995. PMID: 8562832 Review.
Cited by
-
eIF5 is a dual function GAP and GDI for eukaryotic translational control.Small GTPases. 2010 Sep;1(2):118-123. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.1.2.13783. Small GTPases. 2010. PMID: 21686265 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic AMP response element-binding protein prevents endothelial permeability increase through transcriptional controlling p190RhoGAP expression.Blood. 2012 Jan 5;119(1):308-19. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-339473. Epub 2011 Nov 2. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22049513 Free PMC article.
-
RhoGDI phosphorylation by PKC promotes its interaction with death receptor p75NTR to gate axon growth and neuron survival.EMBO Rep. 2024 Mar;25(3):1490-1512. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00064-2. Epub 2024 Jan 22. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38253689 Free PMC article.
-
A functional siRNA screen identifies RhoGTPase-associated genes involved in thrombin-induced endothelial permeability.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 26;13(7):e0201231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201231. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30048510 Free PMC article.
-
Cholecystokinin-mediated RhoGDI phosphorylation via PKCα promotes both RhoA and Rac1 signaling.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 11;8(6):e66029. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066029. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chikumi, H., J. Vázquez-Prado, J.-M. Servitja, H. Miyazaki, and J. S. Gutkind. 2002. Potent activation of RhoA by Gαq and Gq-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 277:27130-27134. - PubMed
-
- Coughlin, S. R. 2000. Thrombin signalling and protease-activated receptors. Nature 407:258-264. - PubMed
-
- DerMardirossian, C., and G. M. Bokoch. 2005. GDIs: central regulatory molecules in Rho GTPase activation. Trends Cell Biol. 15:356-363. - PubMed
-
- DerMardirossian, C., A. Schnelzer, and G. M. Bokoch. 2004. Phosphorylation of RhoGDI by Pak1 mediates dissociation of Rac GTPase. Mol. Cell 15:117-127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
