HP1alpha guides neuronal fate by timing E2F-targeted genes silencing during terminal differentiation
- PMID: 17627279
- PMCID: PMC1949014
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601789
HP1alpha guides neuronal fate by timing E2F-targeted genes silencing during terminal differentiation
Abstract
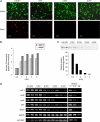
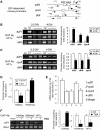
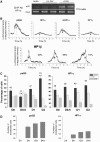
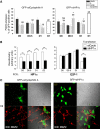
A critical step of neuronal terminal differentiation is the permanent withdrawal from the cell cycle that requires the silencing of genes that drive mitosis. Here, we describe that the alpha isoform of the heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) protein family exerts such silencing on several E2F-targeted genes. Among the different isoforms, HP1alpha levels progressively increase throughout differentiation and take over HP1gamma binding on E2F sites in mature neurons. When overexpressed, only HP1alpha is able to ensure a timed repression of E2F genes. Specific inhibition of HP1alpha expression drives neuronal progenitors either towards death or cell cycle progression, yet preventing the expression of the neuronal marker microtubule-associated protein 2. Furthermore, we provide evidence that this mechanism occurs in cerebellar granule neurons in vivo, during the postnatal development of the cerebellum. Finally, our results suggest that E2F-targeted genes are packaged into higher-order chromatin structures in mature neurons relative to neuroblasts, likely reflecting a transition from a 'repressed' versus 'silenced' status of these genes. Together, these data present new epigenetic regulations orchestrated by HP1 isoforms, critical for permanent cell cycle exit during neuronal differentiation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dynamic and selective interactions of the transcriptional corepressor TIF1 beta with the heterochromatin protein HP1 isotypes during cell differentiation.Differentiation. 2007 Sep;75(7):627-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2007.00166.x. Epub 2007 Mar 23. Differentiation. 2007. PMID: 17381543
-
Rb and p130 control cell cycle gene silencing to maintain the postmitotic phenotype in cardiac myocytes.J Cell Biol. 2011 Aug 8;194(3):407-23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201012049. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21825075 Free PMC article.
-
Differential cooperation between heterochromatin protein HP1 isoforms and MyoD in myoblasts.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 29;283(35):23692-700. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802647200. Epub 2008 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18599480 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the histone tale: HP1α deregulation in breast cancer epigenetics.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(2):189-200. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2014.1001277. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25588111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rb/chromatin connection and epigenetic control: opinion.Oncogene. 2001 May 28;20(24):3128-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204337. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11420729 Review.
Cited by
-
SUMOylation of HP1α supports association with ncRNA to define responsiveness of breast cancer cells to chemotherapy.Oncotarget. 2016 May 24;7(21):30336-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8733. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27107417 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms controlling cell cycle exit upon terminal differentiation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;19(6):697-704. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.10.004. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 18035529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-context specific role of the E2F/Rb pathway in development and disease.Glia. 2010 Mar;58(4):377-90. doi: 10.1002/glia.20933. Glia. 2010. PMID: 19795505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterochromatin protein 1 promotes self-renewal and triggers regenerative proliferation in adult stem cells.J Cell Biol. 2013 Apr 29;201(3):409-25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201207172. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23629965 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of myogenic gene expression by heterochromatin protein 1 alpha.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058319. Epub 2013 Mar 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auth T, Kunkel E, Grummt F (2006) Interaction between HP1alpha and replication proteins in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res 312: 3349–3359 - PubMed
-
- Badugu R, Yoo Y, Singh PB, Kellum R (2005) Mutations in the heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) hinge domain affect HP1 protein interactions and chromosomal distribution. Chromosoma 113: 370–384 - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124 - PubMed
-
- Boutillier AL, Trinh E, Loeffler JP (2002) Constitutive repression of E2F1 transcriptional activity through HDAC proteins is essential for neuronal survival. Ann N Y Acad Sci 973: 438–442 - PubMed
-
- Boutillier AL, Trinh E, Loeffler JP (2003) Selective E2F-dependent gene transcription is controlled by histone deacetylase activity during neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 84: 814–828 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

