FRET-detectable interactions between the ARE binding proteins, HuR and p37AUF1
- PMID: 17626845
- PMCID: PMC1950754
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.501707
FRET-detectable interactions between the ARE binding proteins, HuR and p37AUF1
Abstract
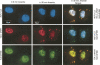
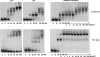
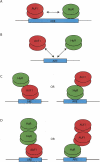
A number of highly regulated gene classes are regulated post-transcriptionally at the level of mRNA stability. A central feature in these mRNAs is the presence of A+U-rich elements (ARE) within their 3' UTRs. Two ARE binding proteins, HuR and AUF1, are associated with mRNA stabilization and destabilization, respectively. Previous studies have demonstrated homomultimerization of each protein and the capacity to bind simultaneous or competitively to a single ARE. To investigate this possibility further, cell biological and biophysical approaches were undertaken. Protein-protein interaction was monitored by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and by immunocytochemistry in live and fixed cells using fluorescently labeled CFP/YFP fusion proteins of HuR and p37AUF1. Strong nuclear FRET between HuR/HuR and AUF1/AUF1 homodimers as well as HuR/AUF1 heterodimers was observed. Treatment with the MAP kinase activator, anisomycin, which commonly stabilizes ARE-containing mRNAs, caused rapid nuclear to cytoplasmic shuttling of HuR. AUF1 also underwent shuttling, but on a longer time scale. After shuttling, HuR/HuR, AUF1/AUF1, and HuR/AUF1, FRET was also observed in the cytoplasm. In further studies, arsenite rapidly induced the formation of stress granules containing HuR and TIA-1 but not AUF1. The current studies demonstrate that two mRNA binding proteins, HuR and AUF1, are colocalized and are capable of functional interaction in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. FRET-based detection of AUF1/HuR interaction may serve as a basis of opening up new dimensions in delineating the functional interaction of mRNA binding proteins with RNA turnover.
Figures
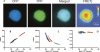
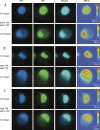
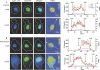
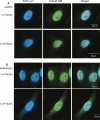


Similar articles
-
Intracellular localization and interaction of mRNA binding proteins as detected by FRET.BMC Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 15;11:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-11-69. BMC Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20843363 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of RNA-binding proteins HuR and AUF1 with the human ATF3 mRNA 3'-untranslated region regulates its amino acid limitation-induced stabilization.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 14;280(41):34609-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507802200. Epub 2005 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16109718 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines regulate the stability of JunD mRNA by modulating the competitive binding of its 3' untranslated region to HuR and AUF1.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;30(21):5021-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00807-10. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20805360 Free PMC article.
-
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) and HuR RNA operons collaboratively regulate the expression of survival and proliferative genes.Cell Cycle. 2009 Apr 1;8(7):960-1. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19287207 Review. No abstract available.
-
Physiological networks and disease functions of RNA-binding protein AUF1.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 Jul-Aug;5(4):549-64. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1230. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24687816 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional control of gene expression by AUF1: mechanisms, physiological targets, and regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul;1829(6-7):680-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23246978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of HuR as a new mechanism of doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2012 Mar 21;11:13. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-13. Mol Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22436134 Free PMC article.
-
AUF1 regulation of coding and noncoding RNA.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Mar;8(2):10.1002/wrna.1393. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1393. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 27620010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HuR regulates the expression of stress-sensitive genes and mediates inflammatory response in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 13;107(15):6858-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000444107. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20351266 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mRNA binding proteins that regulate the stability of LDL receptor mRNA through AU-rich elements.J Lipid Res. 2009 May;50(5):820-31. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800375-JLR200. Epub 2009 Jan 13. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19141871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham, W.T., Gilbert, E.M., Lowes, B.D., Minobe, W.A., Larrabee, P., Roden, R.L., Dutcher, D., Sederberg, J., Lindenfeld, J.A., Wolfel, E.E., et al. Coordinate changes in Myosin heavy chain isoform gene expression are selectively associated with alterations in dilated cardiomyopathy phenotype. Mol. Med. 2002;8:750–760. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atasoy, U., Watson, J., Patel, D., Keene, J.D. ELAV protein HuA (HuR) can redistribute between nucleus and cytoplasm and is upregulated during serum stimulation and T cell activation. J. Cell Sci. 1998;111:3145–3156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
