The GTPase Rac regulates the proliferation and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 17622308
- PMCID: PMC1906689
- DOI: 10.2119/2007–00025.Chan
The GTPase Rac regulates the proliferation and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
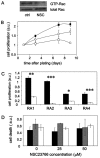
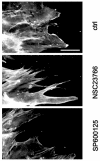
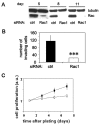
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) isolated from joints of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients display proliferative and invasive properties reminiscent of those of malignant tumor cells. Rac small GTPases play an important role in tumor cell proliferation and invasion. We therefore investigated the potential role of Rac proteins in the proliferative and invasive behavior of RA-FLS. We showed that inhibiting Rac activity with the Rac-specific small molecule inhibitor NSC23766 causes a strong inhibition of RA-FLS proliferation, without affecting cell survival. Rac inhibition also results in a strong reduction in RA-FLS invasion through reconstituted extracellular matrix and a less marked inhibition of two-dimensional migration as measured by monolayer wound healing. We also showed that small interfering RNA-mediated depletion of Rac1 inhibits RA-FLS proliferation and invasion to a similar extent as NSC23766. These results demonstrate for the first time that Rac proteins play an important role in the aggressive behavior of FLS isolated from RA patients. In addition, we observed that inhibiting Rac proteins prevents JNK activation and that the JNK inhibitor SP600125 strongly inhibits RA-FLS invasion, suggesting that Rac-mediated JNK activation contributes to the role of Rac proteins in the invasive behavior of RA-FLS. In conclusion, Rac-controlled signaling pathways may present a new source of drug targets for therapeutic intervention in RA.
Figures

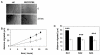
Similar articles
-
Tetrandrine inhibits migration and invasion of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through down-regulating the expressions of Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA GTPases and activation of the PI3K/Akt and JNK signaling pathways.Chin J Nat Med. 2015 Nov;13(11):831-841. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(15)30087-X. Chin J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26614458
-
mTOR regulates the invasive properties of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Med. 2010 Sep-Oct;16(9-10):352-8. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00049. Epub 2010 May 27. Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20517583 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p21-activated kinase 1 in regulating the migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012 Jul;51(7):1170-80. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes031. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 22416254
-
Development of EHop-016: a small molecule inhibitor of Rac.Enzymes. 2013;33 Pt A(Pt A):117-46. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416749-0.00006-3. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Enzymes. 2013. PMID: 25033803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-function based design of small molecule inhibitors targeting Rho family GTPases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(11):1109-16. doi: 10.2174/156802606777812095. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842149 Review.
Cited by
-
The arthritis severity locus Cia5d is a novel genetic regulator of the invasive properties of synovial fibroblasts.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Aug;58(8):2296-306. doi: 10.1002/art.23610. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18668563 Free PMC article.
-
Smoothened Regulates Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via Activation of Rho GTPase Signaling.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 15;8:159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00159. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28261216 Free PMC article.
-
The arthritis severity locus Cia5a regulates the expression of inflammatory mediators including Syk pathway genes and proteases in pristane-induced arthritis.BMC Genomics. 2012 Dec 19;13:710. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-710. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23249408 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Carbon Nanoparticles Inhibit Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Invasiveness and Reduce Disease Severity in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 16;9(10):1005. doi: 10.3390/antiox9101005. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33081234 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative omics analysis of rheumatoid arthritis identifies non-obvious therapeutic targets.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 22;10(4):e0124254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124254. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25901943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burmester GR, et al. The tissue architecture of synovial membranes in inflammatory and non-inflammatory joint diseases. I The localization of the major synovial cell populations as detected by monoclonal reagents directed toward Ia and monocyte-macrophage antigens. Rheumatol Int. 1983;3:173–81. - PubMed
-
- Gulko PS, Seki H, Winchester R. The role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. In: Firestein GS, Panayi GS, Wollheim FA, editors. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Oxford University Press; 2000. pp. 113–35.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
