Linking of autophagy to ubiquitin-proteasome system is important for the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell viability
- PMID: 17620365
- PMCID: PMC1934546
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070188
Linking of autophagy to ubiquitin-proteasome system is important for the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell viability
Abstract
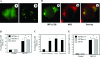
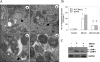
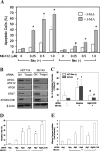
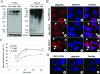
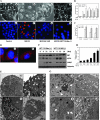
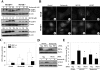
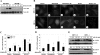
Two major protein degradation systems exist in cells, the ubiquitin proteasome system and the autophagy machinery. Here, we investigated the functional relationship of the two systems and the underlying mechanisms. Proteasome inhibition activated autophagy, suggesting that the two are functionally coupled. Autophagy played a compensatory role as suppression of autophagy promoted the accumulation of polyubiquitinated protein aggregates. Autophagy was likely activated in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress caused by misfolded proteins during proteasome inhibition. Suppression of a major unfolded protein response pathway mediated by IRE1 by either gene deletion or RNA interference dramatically suppressed the activation of autophagy by proteasome inhibitors. Interestingly, c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) but not XBP-1, both of which are the known downstream targets of IRE1, seemed to participate in autophagy induction by proteasome inhibitors. Finally, proteasome inhibitor-induced autophagy was important for controlling endoplasmic reticulum stress and reducing cell death in cancer cells. Our studies thus provide a mechanistic view and elucidate the functional significance of the link between the two protein degradation systems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The GST-BHMT assay reveals a distinct mechanism underlying proteasome inhibition-induced macroautophagy in mammalian cells.Autophagy. 2015;11(5):812-32. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034402. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25984893 Free PMC article.
-
Lafora disease proteins malin and laforin are recruited to aggresomes in response to proteasomal impairment.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 Apr 1;16(7):753-62. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm006. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17337485
-
Overexpression of endoplasmic reticulum-resident chaperone attenuates cardiomyocyte death induced by proteasome inhibition.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Sep 1;79(4):600-10. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn128. Epub 2008 May 28. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18508854
-
Ubiquitination-Proteasome System (UPS) and Autophagy Two Main Protein Degradation Machineries in Response to Cell Stress.Cells. 2022 Mar 1;11(5):851. doi: 10.3390/cells11050851. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sorting, recognition and activation of the misfolded protein degradation pathways through macroautophagy and the proteasome.Autophagy. 2008 Feb;4(2):141-50. doi: 10.4161/auto.5190. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Autophagy. 2008. PMID: 17986870 Review.
Cited by
-
siRNA silencing of proteasome maturation protein (POMP) activates the unfolded protein response and constitutes a model for KLICK genodermatosis.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029471. Epub 2012 Jan 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22235297 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging evidence for endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Apr 15;302(8):L721-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00410.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22287606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of autophagy and innate immunity in Crohn's disease: a key immunobiologic feature.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul 28;19(28):4447-54. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4447. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23901219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular basis for selective inhibition of unconventional mRNA splicing by an IRE1-binding small molecule.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Apr 10;109(15):E869-78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115623109. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22315414 Free PMC article.
-
Selective autophagy: talking with the UPS.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013 Sep;67(1):3-13. doi: 10.1007/s12013-013-9623-7. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23709310 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Meusser B, Hirsch C, Jarosch E, Sommer T. ERAD: the long road to destruction. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:766–772. - PubMed
-
- Schroder M, Kaufman RJ. The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:739–789. - PubMed
-
- Harding HP, Calfon M, Urano F, Novoa I, Ron D. Transcriptional and translational control in the mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002;18:575–599. - PubMed
-
- Rao RV, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE. Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:372–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

