IL-2 immunotoxin denileukin diftitox reduces regulatory T cells and enhances vaccine-mediated T-cell immunity
- PMID: 17616639
- PMCID: PMC2200901
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-06-094615
IL-2 immunotoxin denileukin diftitox reduces regulatory T cells and enhances vaccine-mediated T-cell immunity
Abstract
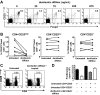
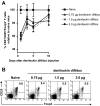
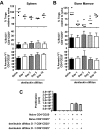
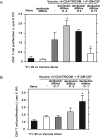
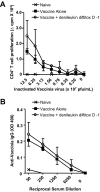
CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells have been implicated in the lack of effective antitumor immunity. Denileukin diftitox (DAB(389)IL-2), a fusion protein of interleukin 2 (IL-2) and diphtheria toxin, provides a means of targeting Treg cells. In this study, we examined (1) the effect of denileukin diftitox on the deletion of Treg cells in various lymphoid compartments and (2) the dose scheduling of denileukin diftitox in combination with a recombinant poxviral vaccine to enhance antigen-specific immune responses. Treg cells in spleen, peripheral blood, and bone marrow of normal C57BL/6 mice were variously reduced after a single intraperitoneal injection of denileukin diftitox; the reduction was evident within 24 hours and lasted approximately 10 days. Injection of denileukin diftitox 1 day before vaccination enhanced antigen-specific T-cell responses above levels induced by vaccination alone. These studies show for the first time in a murine model (1) the differential effects of denileukin diftitox on Treg cells in different cellular compartments, (2) the advantage of combining denileukin diftitox with a vaccine to enhance antigen-specific T-cell immune responses, (3) the lack of inhibition by denileukin diftitox of host immune responses directed against a live viral vector, and (4) the importance of dose scheduling of denileukin diftitox when used in combination with a vaccine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depletion of human regulatory T cells specifically enhances antigen-specific immune responses to cancer vaccines.Blood. 2008 Aug 1;112(3):610-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-01-135319. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18519811 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Upfront denileukin diftitox as in vivo regulatory T-cell depletion in order to enhance vaccination effects in a canine allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation model.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012 Jan 15;145(1-2):233-40. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2011.11.009. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 22173275
-
Differential effects of denileukin diftitox IL-2 immunotoxin on NK and regulatory T cells in nonhuman primates.J Immunol. 2012 Jun 15;188(12):6063-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200656. Epub 2012 May 14. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22586034 Free PMC article.
-
Denileukin diftitox.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000 Jan-Feb;1(1):67-72; discussion 73. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200001010-00008. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 11702307 Review.
-
Optimizing denileukin diftitox (Ontak) therapy.Future Oncol. 2008 Aug;4(4):457-69. doi: 10.2217/14796694.4.4.457. Future Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18684057 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling promotes central memory T cell differentiation.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 1;191(5):2299-307. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300472. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23904158 Free PMC article.
-
Timed sequential treatment with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and an allogeneic granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-secreting breast tumor vaccine: a chemotherapy dose-ranging factorial study of safety and immune activation.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Dec 10;27(35):5911-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.3494. Epub 2009 Oct 5. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19805669 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
TGF-beta utilizes SMAD3 to inhibit CD16-mediated IFN-gamma production and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in human NK cells.J Immunol. 2008 Sep 15;181(6):3784-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.6.3784. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18768831 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of CD25⁺ T cells from hematopoietic stem cell grafts increases posttransplantation vaccine-induced immunity to neuroblastoma.Blood. 2011 Jun 23;117(25):6952-62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-326108. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21521781 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of murine allergic airway disease by IL-2:anti-IL-2 monoclonal antibody-induced regulatory T cells.J Immunol. 2008 Nov 15;181(10):6942-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.6942. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18981114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:345–352. - PubMed
-
- Gavin M, Rudensky A. Control of immune homeostasis by naturally arising regulatory CD4+ T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15:690–696. - PubMed
-
- Woo EY, Chu CS, Goletz TJ, et al. Regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4766–4772. - PubMed
-
- Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, et al. Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 2002;169:2756–2761. - PubMed
-
- Ichihara F, Kono K, Takahashi A, Kawaida H, Sugai H, Fujii H. Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with gastric and esophageal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:4404–4408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

