Infection and coaccumulation of tobacco mosaic virus proteins alter microRNA levels, correlating with symptom and plant development
- PMID: 17615233
- PMCID: PMC1924585
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705114104
Infection and coaccumulation of tobacco mosaic virus proteins alter microRNA levels, correlating with symptom and plant development
Abstract
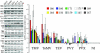
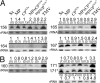
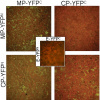
Infections by plant virus generally cause disease symptoms by interfering with cellular processes. Here we demonstrated that infection of Nicotiana tabacum (N.t) by plant viruses representative of the Tobamoviridae, Potyviridae, and Potexviridae families altered accumulation of certain microRNAs (miRNAs). A correlation was observed between symptom severity and alteration in levels of miRNAs 156, 160, 164,166, 169, and 171 that is independent of viral posttranscriptional gene silencing suppressor activity. Hybrid transgenic plants that produced tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) movement protein (MP) plus coat protein (CP)(T42W) (a variant of CP) exhibited disease-like phenotypes, including abnormal plant development. Grafting studies with a plant line in which both transgenes are silenced confirmed that the disease-like phenotypes are due to the coexpression of CP and MP. In hybrid MPxCP(T42W) plants and TMV-infected plants, miRNAs 156, 164, 165, and 167 accumulated to higher levels compared with nontransgenic and noninfected tissues. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays revealed that MP interacts with CP(T42W) in vivo and leads to the hypothesis that complexes formed between MP and CP caused increases in miRNAs that result in disease symptoms. This work presents evidence that virus infection and viral proteins influence miRNA balance without affecting posttranscriptional gene silencing and contributes to the hypothesis that viruses exploit miRNA pathways during pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transgenic expression of Tobacco mosaic virus capsid and movement proteins modulate plant basal defense and biotic stress responses in Nicotiana tabacum.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2012 Oct;25(10):1370-84. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-12-0075-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2012. PMID: 22712510
-
Characterization of mutant tobacco mosaic virus coat protein that interferes with virus cell-to-cell movement.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 19;99(6):3645-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062041499. Epub 2002 Mar 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11891326 Free PMC article.
-
The 2b silencing suppressor of a mild strain of Cucumber mosaic virus alone is sufficient for synergistic interaction with Tobacco mosaic virus and induction of severe leaf malformation in 2b-transgenic tobacco plants.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011 Jun;24(6):685-93. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-10-0290. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011. PMID: 21341985
-
Coat-protein-mediated resistance to tobacco mosaic virus: discovery mechanisms and exploitation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Mar 29;354(1383):659-64. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0418. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10212946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and study of tobacco mosaic virus movement function by complementation tests.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Mar 29;354(1383):629-35. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0414. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10212942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of microRNA-mediated gene expression regulation in the pathological development of stem canker disease in Populus trichocarpa.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044968. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028709 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA160 is associated with local defense and systemic acquired resistance against Phytophthora infestans infection in potato.J Exp Bot. 2018 Apr 9;69(8):2023-2036. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery025. J Exp Bot. 2018. PMID: 29390146 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of microRNAs from in vitro-grown pear shoots infected with Apple stem grooving virus in response to high temperature using small RNA sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2015 Nov 16;16:945. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2126-8. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26573813 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of microRNAs in response to Papaya ringspot virus infection in differentially responding genotypes of papaya (Carica papaya L.) and its wild relative.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 20;15:1398437. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1398437. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38966149 Free PMC article.
-
Pol II-directed short RNAs suppress the nuclear export of mRNA.Plant Mol Biol. 2010 Dec;74(6):591-603. doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9700-x. Epub 2010 Oct 17. Plant Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20953971
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

