Transforming growth factor-beta and fibrosis
- PMID: 17589920
- PMCID: PMC4172611
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3056
Transforming growth factor-beta and fibrosis
Abstract
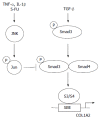
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), a prototype of multifunctional cytokine, is a key regulator of extracellular matrix (ECM) assembly and remodeling. Specifically, TGF-beta isoforms have the ability to induce the expression of ECM proteins in mesenchymal cells, and to stimulate the production of protease inhibitors that prevent enzymatic breakdown of the ECM. Elevated TGF-beta expression in affected organs, and subsequent deregulation of TGF-beta functions, correlates with the abnormal connective tissue deposition observed during the onset of fibrotic diseases. During the last few years, tremendous progress has been made in the understanding of the molecular aspects of intracellular signaling downstream of the TGF-beta receptors. In particular, Smad proteins, TGF-beta receptor kinase substrates that translocate into the cell nucleus to act as transcription factors, have been studied extensively. The role of Smad3 in the transcriptional regulation of type I collagen gene expression and in the development of fibrosis, demonstrated both in vitro and in animal models with a targeted deletion of Smad3, is of critical importance because it may lead to novel therapeutic strategies against these diseases. This review focuses on the mechanisms underlying Smad modulation of fibrillar collagen expression and how it relates to fibrotic processes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tissue toxicity induced by ionizing radiation to the normal intestine: understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms to improve the medical management.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jun 14;13(22):3031-2. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3031. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17589916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling through the Smad pathway: role in extracellular matrix gene expression and regulation.J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Feb;118(2):211-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.01641.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 11841535 Review.
-
The role of TGF-beta signaling in the pathogenesis of fibrosis in scleroderma.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2002;50(5):325-31. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2002. PMID: 12455866 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling through the Smad proteins: role in systemic sclerosis.Autoimmun Rev. 2006 Oct;5(8):563-9. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Jul 5. Autoimmun Rev. 2006. PMID: 17027893 Review.
-
Pathogenesis of fibrosis: role of TGF-beta and CTGF.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002 Nov;14(6):681-5. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200211000-00009. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002. PMID: 12410091 Review.
-
Control of connective tissue gene expression by TGF beta: role of Smad proteins in fibrosis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002 Apr;4(2):143-9. doi: 10.1007/s11926-002-0010-4. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002. PMID: 11890880 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Dec 1;303(11):G1175-87. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00313.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23019192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Molecular Mechanisms, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicology and Plant Sources of Juglanin: Current Landscape and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 25;25(19):10323. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910323. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural changes in alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonist-treated human prostatic stroma.Clin Exp Med. 2010 Jun;10(2):99-106. doi: 10.1007/s10238-009-0073-x. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Clin Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 19826760
-
miR-98-5p as a novel biomarker suppress liver fibrosis by targeting TGFβ receptor 1.Hepatol Int. 2022 Jun;16(3):614-626. doi: 10.1007/s12072-021-10277-5. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Hepatol Int. 2022. PMID: 35188624
-
Amygdalin Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis through Inhibiting Activation of TGF-β/Smad Signaling.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Apr;29(4):316-324. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-3304-y. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 34816365
References
-
- Uitto J, Kouba D. Cytokine modulation of extracellular matrix gene expression: relevance to fibrotic skin diseases. J Dermatol Sci. 2000;24 Suppl 1:S60–S69. - PubMed
-
- Verrecchia F, Mauviel A. TGF-beta and TNF-alpha: antagonistic cytokines controlling type I collagen gene expression. Cell Signal. 2004;16:873–880. - PubMed
-
- Verrecchia F, Mauviel A. Control of connective tissue gene expression by TGF beta: role of Smad proteins in fibrosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002;4:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Verrecchia F, Mauviel A. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling through the Smad pathway: role in extracellular matrix gene expression and regulation. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118:211–215. - PubMed
-
- LeRoy EC, Trojanowska MI, Smith EA. Cytokines and human fibrosis. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1990;1:215–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical