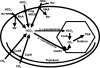
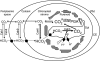
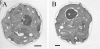
Proposed carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 17557885
- PMCID: PMC1951128
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00064-07
Proposed carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: inorganic carbon transport and CO2 recapture.Photosynth Res. 2011 Sep;109(1-3):115-22. doi: 10.1007/s11120-011-9643-3. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Photosynth Res. 2011. PMID: 21409558 Review.
-
Expression activation and functional analysis of HLA3, a putative inorganic carbon transporter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Plant J. 2015 Apr;82(1):1-11. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12788. Plant J. 2015. PMID: 25660294
-
Ccm1, a regulatory gene controlling the induction of a carbon-concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by sensing CO2 availability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):5347-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.081593498. Epub 2001 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11287669 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon-concentrating mechanism in a green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, revealed by transcriptome analyses.J Basic Microbiol. 2009 Feb;49(1):42-51. doi: 10.1002/jobm.200800352. J Basic Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19253331 Review.
-
[Mechanism of CO2-responsive transcriptional regulation in photosynthetic organisms: carbon-concentrating mechanism in a green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2005 Jul;50(8):958-65. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2005. PMID: 16001801 Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Complex mathematical analysis of photobioreactor system.Eng Life Sci. 2018 Sep 25;19(12):844-859. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201800044. eCollection 2019 Dec. Eng Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 32624977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isogamy in large and complex volvocine algae is consistent with the gamete competition theory of the evolution of anisogamy.Proc Biol Sci. 2018 Nov 7;285(1890):20181954. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2018.1954. Proc Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404882 Free PMC article.
-
The carbonic anhydrase isoforms of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: intracellular location, expression, and physiological roles.Photosynth Res. 2011 Sep;109(1-3):133-49. doi: 10.1007/s11120-011-9635-3. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Photosynth Res. 2011. PMID: 21365258 Review.
-
Carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: inorganic carbon transport and CO2 recapture.Photosynth Res. 2011 Sep;109(1-3):115-22. doi: 10.1007/s11120-011-9643-3. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Photosynth Res. 2011. PMID: 21409558 Review.
-
Regulation of cyclic electron flow in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under fluctuating carbon availability.Photosynth Res. 2013 Nov;117(1-3):449-59. doi: 10.1007/s11120-013-9932-0. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Photosynth Res. 2013. PMID: 24113925
References
-
- Adams, J. E., S. L. Colombo, C. B. Mason, R. A. Ynalvez, B. Tural, and J. V. Moroney. 2005. A mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii that cannot acclimate to low CO2 conditions has an insertion in the Hdh1 gene. Funct. Plant Biol. 32:55-66. - PubMed
-
- Aizawa, K. S., and S. Miyachi. 1986. Carbonic anhydrase and CO2 concentrating mechanisms in microalgae and cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 39:215-233.
-
- Asamiziu, E., K. Miura, K. Kucho, Y. Inoue, H. Fukuzawa, K. Ohyama, Y. Nakamura, and S. Tabata. 2000. Generation of expressed sequence tags from low-CO2 and high-CO2 adapted cells of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. DNA Res. 7:305-307. - PubMed
-
- Badger, M. R., and G. D. Price. 1994. The role of carbonic anhydrase in photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 45:369-392.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

