Spatial preferences of microRNA targets in 3' untranslated regions
- PMID: 17555584
- PMCID: PMC1904200
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-152
Spatial preferences of microRNA targets in 3' untranslated regions
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs are an important class of regulatory RNAs which repress animal genes by preferentially interacting with complementary sequence motifs in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs. Computational methods have been developed which can successfully predict which microRNA may target which mRNA on a genome-wide scale.
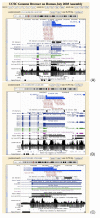
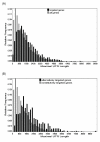
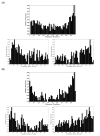
Results: We address how predicted target sites may be affected by alternative polyadenylation events changing the 3'UTR sequence. We find that two thirds of targeted genes have alternative 3'UTRs, with 40% of predicted target sites located in alternative UTR segments. We propose three classes based on whether the target sites fall within constitutive and/or alternative UTR segments, and examine the spatial distribution of predicted targets in alternative UTRs. In particular, there is a strong preference for targets to be located in close vicinity of the stop codon and the polyadenylation sites.
Conclusion: The transcript diversity seen in non-coding regions, as well as the relative location of miRNA target sites defined by it, has a potentially large impact on gene regulation by miRNAs and should be taken into account when defining, predicting or validating miRNA targets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolution of Hox post-transcriptional regulation by alternative polyadenylation and microRNA modulation within 12 Drosophila genomes.Mol Biol Evol. 2011 Sep;28(9):2453-60. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr073. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 21436120
-
Reprogramming of 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs by alternative polyadenylation in generation of pluripotent stem cells from different cell types.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 23;4(12):e8419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008419. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20037631 Free PMC article.
-
Formation, regulation and evolution of Caenorhabditis elegans 3'UTRs.Nature. 2011 Jan 6;469(7328):97-101. doi: 10.1038/nature09616. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21085120 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of human microRNA targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:101-13. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:101. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957370 Review.
-
Small but influential: the role of microRNAs on gene regulatory network and 3'UTR evolution.J Genet Genomics. 2009 Jan;36(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60001-1. J Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19161940 Review.
Cited by
-
Relative contribution of sequence and structure features to the mRNA binding of Argonaute/EIF2C-miRNA complexes and the degradation of miRNA targets.Genome Res. 2009 Nov;19(11):2009-20. doi: 10.1101/gr.091181.109. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19767416 Free PMC article.
-
The survivin -31 snp in human colorectal cancer correlates with survivin splice variant expression and improved overall survival.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011 Aug;34(4):381-91. doi: 10.1007/s13402-011-0038-4. Epub 2011 May 3. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011. PMID: 21538024
-
Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions--beyond repression of gene expression.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Sep;15(9):599-612. doi: 10.1038/nrg3765. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25022902 Review.
-
Fragile X protein family member FXR1P is regulated by microRNAs.RNA. 2010 Aug;16(8):1530-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.2022210. Epub 2010 Jun 2. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20519410 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of targeting by endogenous and exogenous microRNAs and siRNAs.RNA. 2007 Nov;13(11):1894-910. doi: 10.1261/rna.768207. Epub 2007 Sep 13. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17872505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Muller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature. 2000;408:86–89. doi: 10.1038/35040556. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

