The A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP)-Lbc-signaling complex mediates alpha1 adrenergic receptor-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
- PMID: 17537920
- PMCID: PMC1891209
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0701099104
The A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP)-Lbc-signaling complex mediates alpha1 adrenergic receptor-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
Abstract
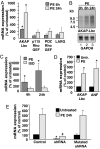
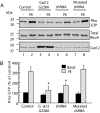
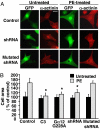
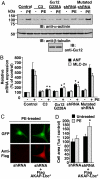
In response to various pathological stresses, the heart undergoes a pathological remodeling process that is associated with cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Because cardiac hypertrophy can progress to heart failure, a major cause of lethality worldwide, the intracellular signaling pathways that control cardiomyocyte growth have been the subject of intensive investigation. It has been known for more than a decade that the small molecular weight GTPase RhoA is involved in the signaling pathways leading to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Although some of the hypertrophic pathways activated by RhoA have now been identified, the identity of the exchange factors that modulate its activity in cardiomyocytes is currently unknown. In this study, we show that AKAP-Lbc, an A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) with an intrinsic Rho-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity, is critical for activating RhoA and transducing hypertrophic signals downstream of alpha1-adrenergic receptors (ARs). In particular, our results indicate that suppression of AKAP-Lbc expression by infecting rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocytes with lentiviruses encoding AKAP-Lbc-specific short hairpin RNAs strongly reduces both alpha1-AR-mediated RhoA activation and hypertrophic responses. Interestingly, alpha1-ARs promote AKAP-Lbc activation via a pathway that requires the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein G12. These findings identify AKAP-Lbc as the first Rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) involved in the signaling pathways leading to cardiomyocytes hypertrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A-kinase anchoring protein-Lbc promotes pro-fibrotic signaling in cardiac fibroblasts.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1843(2):335-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24269843
-
AKAP-Lbc: a molecular scaffold for the integration of cyclic AMP and Rho transduction pathways.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):603-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16460837 Review.
-
RGS2 is upregulated by and attenuates the hypertrophic effect of alpha1-adrenergic activation in cultured ventricular myocytes.Cell Signal. 2006 Oct;18(10):1655-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.01.012. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16517124
-
AKAP-Lbc mediates protection against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte toxicity.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Dec;1864(12):2336-2346. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28923249
-
The alpha1-adrenergic receptors in cardiac hypertrophy: signaling mechanisms and functional implications.Cell Signal. 2015 Oct;27(10):1984-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 26169957 Review.
Cited by
-
Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2 (Shp2) is a component of the A-kinase-anchoring protein (AKAP)-Lbc complex and is inhibited by protein kinase A (PKA) under pathological hypertrophic conditions in the heart.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40535-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.385641. Epub 2012 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23045525 Free PMC article.
-
The α1-adrenergic receptors: diversity of signaling networks and regulation.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010 Dec;30(6):410-9. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2010.518152. Epub 2010 Oct 18. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2010. PMID: 20954794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein-dependent and G protein-independent signaling pathways and their impact on cardiac function.Circ Res. 2011 Jul 8;109(2):217-30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.231225. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21737817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anchored protein kinase A signalling in cardiac cellular electrophysiology.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Nov;18(11):2135-46. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12365. Epub 2014 Sep 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25216213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RhoA Activation Sensitizes Cells to Proteotoxic Stimuli by Abrogating the HSF1-Dependent Heat Shock Response.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 20;10(7):e0133553. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133553. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26193369 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

