ATMIN defines an NBS1-independent pathway of ATM signalling
- PMID: 17525732
- PMCID: PMC1894771
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601733
ATMIN defines an NBS1-independent pathway of ATM signalling
Abstract
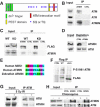
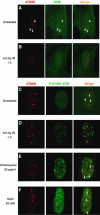
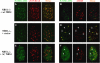
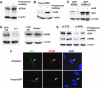
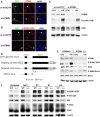
The checkpoint kinase ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) transduces genomic stress signals to halt cell cycle progression and promote DNA repair in response to DNA damage. Here, we report the characterisation of an essential cofactor for ATM, ATMIN (ATM INteracting protein). ATMIN interacts with ATM through a C-terminal motif, which is also present in Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS)1. ATMIN and ATM co-localised in response to ATM activation by chloroquine and hypotonic stress, but not after induction of double-strand breaks by ionising radiation (IR). ATM/ATMIN complex disruption by IR was attenuated in cells with impaired NBS1 function, suggesting competition of NBS1 and ATMIN for ATM binding. ATMIN protein levels were reduced in ataxia telangiectasia cells and ATM protein levels were low in primary murine fibroblasts lacking ATMIN, indicating reciprocal stabilisation. Whereas phosphorylation of Smc1, Chk2 and p53 was normal after IR in ATMIN-deficient cells, basal ATM activity and ATM activation by hypotonic stress and inhibition of DNA replication was impaired. Thus, ATMIN defines a novel NBS1-independent pathway of ATM signalling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATMINistrating ATM signalling: regulation of ATM by ATMIN.Cell Cycle. 2008 Nov 15;7(22):3483-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.22.7044. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 19001856 Review.
-
ATM phosphorylates p95/nbs1 in an S-phase checkpoint pathway.Nature. 2000 Apr 6;404(6778):613-7. doi: 10.1038/35007091. Nature. 2000. PMID: 10766245
-
E2F1 uses the ATM signaling pathway to induce p53 and Chk2 phosphorylation and apoptosis.Mol Cancer Res. 2004 Apr;2(4):203-14. Mol Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15140942
-
Competition between NBS1 and ATMIN controls ATM signaling pathway choice.Cell Rep. 2012 Dec 27;2(6):1498-504. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.11.002. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Cell Rep. 2012. PMID: 23219553
-
The ATM-dependent DNA damage signaling pathway.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:99-109. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2005.70.002. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005. PMID: 16869743 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factor ATMIN facilitates chemoresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 6;15(2):112. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06496-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38321024 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbed hematopoiesis in mice lacking ATMIN.Blood. 2016 Oct 20;128(16):2017-2021. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-672980. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27581360 Free PMC article.
-
The Phosphorylated Form of the Histone H2AX (γH2AX) in the Brain from Embryonic Life to Old Age.Molecules. 2021 Nov 27;26(23):7198. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237198. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATMIN: a new tumor suppressor in developing B cells.Cancer Cell. 2011 May 17;19(5):569-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.05.002. Cancer Cell. 2011. PMID: 21575856 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
ATM, radiation, and the risk of second primary breast cancer.Int J Radiat Biol. 2017 Oct;93(10):1121-1127. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2017.1344363. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Int J Radiat Biol. 2017. PMID: 28627265 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alderton GK, Joenje H, Varon R, Borglum AD, Jeggo PA, O'Driscoll M (2004) Seckel syndrome exhibits cellular features demonstrating defects in the ATR-signalling pathway. Hum Mol Genet 13: 3127–3138 - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB (2003) DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421: 499–506 - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB (2004) Initiating cellular stress responses. Cell 118: 9–17 - PubMed
-
- Behrens A, Sibilia M, Wagner EF (1999) Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet 21: 326–329 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

