Regulation of glutamate receptor B pre-mRNA splicing by RNA editing
- PMID: 17517775
- PMCID: PMC1920255
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm314
Regulation of glutamate receptor B pre-mRNA splicing by RNA editing
Abstract
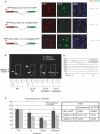
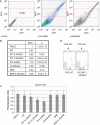
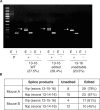
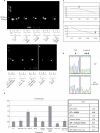
RNA-editing enzymes of the ADAR family convert adenosines to inosines in double-stranded RNA substrates. Frequently, editing sites are defined by base-pairing of the editing site with a complementary intronic region. The glutamate receptor subunit B (GluR-B) pre-mRNA harbors two such exonic editing sites termed Q/R and R/G. Data from ADAR knockout mice and in vitro editing assays suggest an intimate connection between editing and splicing of GluR-B pre-mRNA. By comparing the events at the Q/R and R/G sites, we can show that editing can both stimulate and repress splicing efficiency. The edited nucleotide, but not ADAR binding itself, is sufficient to exert this effect. The presence of an edited nucleotide at the R/G site reduces splicing efficiency of the adjacent intron facilitating alternative splicing events occurring downstream of the R/G site. Lack of editing inhibits splicing at the Q/R site. Editing of both the Q/R nucleotide and an intronic editing hotspot are required to allow efficient splicing. Inefficient intron removal may ensure that only properly edited mRNAs become spliced and exported to the cytoplasm.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The C-terminal domain of RNA Pol II helps ensure that editing precedes splicing of the GluR-B transcript.RNA. 2007 Jul;13(7):1071-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.404407. Epub 2007 May 24. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17525170 Free PMC article.
-
A mammalian RNA editing enzyme.Nature. 1996 Feb 1;379(6564):460-4. doi: 10.1038/379460a0. Nature. 1996. PMID: 8559253
-
Identification of new targets of Drosophila pre-mRNA adenosine deaminase.Physiol Genomics. 2005 Jan 20;20(2):195-202. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00093.2003. Epub 2004 Nov 2. Physiol Genomics. 2005. PMID: 15522950
-
ADAR-mediated RNA editing in non-coding RNA sequences.Sci China Life Sci. 2013 Oct;56(10):944-52. doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4546-5. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24008387 Review.
-
RNA editing in human cancer: review.APMIS. 2009 Aug;117(8):551-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2009.02505.x. APMIS. 2009. Retraction in: APMIS. 2010 Apr;118(4):337. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2010.02601.x. PMID: 19664125 Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Splicing and editing of ionotropic glutamate receptors: a comprehensive analysis based on human RNA-Seq data.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jul;78(14):5605-5630. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03865-z. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34100982 Free PMC article.
-
Protein recoding by ADAR1-mediated RNA editing is not essential for normal development and homeostasis.Genome Biol. 2017 Sep 5;18(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1301-4. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28874170 Free PMC article.
-
ISVASE: identification of sequence variant associated with splicing event using RNA-seq data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Jun 28;18(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1732-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28659141 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR-deficiency perturbs the global splicing landscape in mouse tissues.Genome Res. 2020 Aug;30(8):1107-1118. doi: 10.1101/gr.256933.119. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Genome Res. 2020. PMID: 32727871 Free PMC article.
-
The ADAR protein family.Genome Biol. 2012 Dec 28;13(12):252. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-12-252. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 23273215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roy SW, Gilbert W. The evolution of spliceosomal introns: patterns, puzzles and progress. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:211–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

