Transcription factor modularity in a gene-centered C. elegans core neuronal protein-DNA interaction network
- PMID: 17513831
- PMCID: PMC1899117
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.6148107
Transcription factor modularity in a gene-centered C. elegans core neuronal protein-DNA interaction network
Abstract
Transcription regulatory networks play a pivotal role in the development, function, and pathology of metazoan organisms. Such networks are comprised of protein-DNA interactions between transcription factors (TFs) and their target genes. An important question pertains to how the architecture of such networks relates to network functionality. Here, we show that a Caenorhabditis elegans core neuronal protein-DNA interaction network is organized into two TF modules. These modules contain TFs that bind to a relatively small number of target genes and are more systems specific than the TF hubs that connect the modules. Each module relates to different functional aspects of the network. One module contains TFs involved in reproduction and target genes that are expressed in neurons as well as in other tissues. The second module is enriched for paired homeodomain TFs and connects to target genes that are often exclusively neuronal. We find that paired homeodomain TFs are specifically expressed in C. elegans and mouse neurons, indicating that the neuronal function of paired homeodomains is evolutionarily conserved. Taken together, we show that a core neuronal C. elegans protein-DNA interaction network possesses TF modules that relate to different functional aspects of the complete network.
Figures
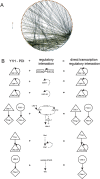
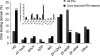
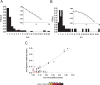


Similar articles
-
A gene-centered C. elegans protein-DNA interaction network.Cell. 2006 Jun 16;125(6):1193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.038. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16777607
-
Mapping and analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans transcription factor sequence specificities.Elife. 2015 Apr 23;4:e06967. doi: 10.7554/eLife.06967. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25905672 Free PMC article.
-
A gene-centered C. elegans protein-DNA interaction network provides a framework for functional predictions.Mol Syst Biol. 2016 Oct 24;12(10):884. doi: 10.15252/msb.20167131. Mol Syst Biol. 2016. PMID: 27777270 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling transcription regulatory networks by protein-DNA and protein-protein interaction mapping.Genome Res. 2006 Dec;16(12):1445-54. doi: 10.1101/gr.5321506. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 17053092 Review.
-
Nuclear factor Y, a key player in neuronal gene regulation.Sci Prog. 2024 Jul-Sep;107(3):368504241264998. doi: 10.1177/00368504241264998. Sci Prog. 2024. PMID: 39043378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis ensemble reverse-engineered gene regulatory network discloses interconnected transcription factors in oxidative stress.Plant Cell. 2014 Dec;26(12):4656-79. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.131417. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25549671 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast one-hybrid assays for gene-centered human gene regulatory network mapping.Nat Methods. 2011 Oct 30;8(12):1050-2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1764. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 22037702 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between transcription factors and microRNAs in genome-scale regulatory networks.Bioessays. 2009 Apr;31(4):435-45. doi: 10.1002/bies.200800212. Bioessays. 2009. PMID: 19274664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-scale spatiotemporal analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans microRNA promoter activity.Genome Res. 2008 Dec;18(12):2005-15. doi: 10.1101/gr.083055.108. Epub 2008 Nov 3. Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18981266 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter-based integration in plant defense regulation.Plant Physiol. 2014 Dec;166(4):1803-20. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.248716. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25352272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akin Z.N., Nazarali A.J., Nazarali A.J. Hox genes and their candidate downstream targets in the developing central nervous system. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005;25:697–741. - PubMed
-
- Albert R., Barabasi A.L., Barabasi A.L. Topology of evolving networks: Local events and universality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000;85:5234–5237. - PubMed
-
- Altun-Gultekin Z., Andachi Y., Tsalik E.L., Pilgrim D., Kohara Y., Hobert O., Andachi Y., Tsalik E.L., Pilgrim D., Kohara Y., Hobert O., Tsalik E.L., Pilgrim D., Kohara Y., Hobert O., Pilgrim D., Kohara Y., Hobert O., Kohara Y., Hobert O., Hobert O. A regulatory cascade of three homeobox genes, ceh-10, ttx-3 and ceh-23, controls cell fate specification of a defined interneuron class in C. elegans. Development. 2001;128:1951–1969. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M., Ball C.A., Blake J.A., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J.M., Davis A.P., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Ball C.A., Blake J.A., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J.M., Davis A.P., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Blake J.A., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J.M., Davis A.P., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J.M., Davis A.P., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Butler H., Cherry J.M., Davis A.P., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Cherry J.M., Davis A.P., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Davis A.P., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Dolinski K., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Dwight S.S., Eppig J.T., Eppig J.T., et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000;25:25–29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babu M.M., Luscombe N.M., Aravind L., Gerstein M., Teichmann S.A., Luscombe N.M., Aravind L., Gerstein M., Teichmann S.A., Aravind L., Gerstein M., Teichmann S.A., Gerstein M., Teichmann S.A., Teichmann S.A. Structure and evolution of transcriptional regulatory networks. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004;14:283–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
