Beta-amyloid disrupted synaptic vesicle endocytosis in cultured hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 17499934
- PMCID: PMC1993833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.03.047
Beta-amyloid disrupted synaptic vesicle endocytosis in cultured hippocampal neurons
Abstract
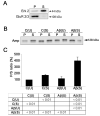
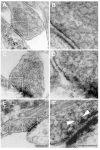
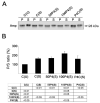
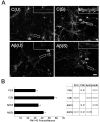
Neuronal death leading to gross brain atrophy is commonly seen in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. Yet, it is becoming increasingly apparent that the pathogenesis of AD involves early and more discrete synaptic changes in affected brain areas. However, the molecular mechanisms that underlie such synaptic dysfunction remain largely unknown. Recently, we have identified dynamin 1, a protein that plays a critical role in synaptic vesicle endocytosis, and hence, in the signaling properties of the synapse, as a potential molecular determinant of such dysfunction in AD. In the present study, we analyzed beta-amyloid (Abeta)-induced changes in synaptic vesicle recycling in rat cultured hippocampal neurons. Our results showed that Abeta, the main component of senile plaques, caused ultrastructural changes indicative of impaired synaptic vesicle endocytosis in cultured hippocampal neurons that have been stimulated by depolarization with high potassium. In addition, Abeta led to the accumulation of amphiphysin in membrane fractions from stimulated hippocampal neurons. Moreover, experiments using FM1-43 showed reduced dye uptake in stimulated hippocampal neurons treated with Abeta when compared with untreated stimulated controls. Similar results were obtained using a dynamin 1 inhibitory peptide suggesting that dynamin 1 depletion caused deficiency in synaptic vesicle recycling not only in Drosophila but also in mammalian neurons. Collectively, these results showed that Abeta caused a disruption of synaptic vesicle endocytosis in cultured hippocampal neurons. Furthermore, we provided evidence suggesting that Abeta-induced dynamin 1 depletion might play an important role in this process.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The novel calpain inhibitor A-705253 potently inhibits oligomeric beta-amyloid-induced dynamin 1 and tau cleavage in hippocampal neurons.Neurochem Int. 2008 Sep;53(3-4):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.06.003. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Neurochem Int. 2008. PMID: 18590784 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-amyloid-induced dynamin 1 depletion in hippocampal neurons. A potential mechanism for early cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 9;280(36):31746-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503259200. Epub 2005 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16002400 Free PMC article.
-
beta-Amyloid-induced dynamin 1 degradation is mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in hippocampal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 22;281(38):28079-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605081200. Epub 2006 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16864575
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
Amyloid-β and Synaptic Vesicle Dynamics: A Cacophonic Orchestra.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(1):1-14. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190771. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31561377 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple effects of β-amyloid on single excitatory synaptic connections in the PFC.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep 3;7:129. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00129. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24027495 Free PMC article.
-
Increased membrane cholesterol might render mature hippocampal neurons more susceptible to beta-amyloid-induced calpain activation and tau toxicity.J Neurosci. 2009 Apr 8;29(14):4640-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0862-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19357288 Free PMC article.
-
iTRAQ analysis of complex proteome alterations in 3xTgAD Alzheimer's mice: understanding the interface between physiology and disease.PLoS One. 2008 Jul 23;3(7):e2750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002750. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18648646 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic convergence and network analysis approach to identify candidate genes in Alzheimer's disease.BMC Genomics. 2014 Mar 15;15(1):199. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-199. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24628925 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of calpain prevents NMDA-induced cell death and beta-amyloid-induced synaptic dysfunction in hippocampal slice cultures.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Apr;159(7):1523-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00652.x. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20233208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battaglia F, Trinchese F, Liu S, Walter S, Nixon RA, Arancio O. Calpain inhibitors, a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: position paper. J Mol Neurosci. 2003;20:357–362. - PubMed
-
- Bennett JA, Dingledine R. Topology profile for a glutamate receptor: three transmembrane domains and a channel-lining reentrant membrane loop. Neuron. 1995;14:373–384. - PubMed
-
- Bensadoun A, Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976;70:241–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

