Animal models and vaccines for SARS-CoV infection
- PMID: 17499378
- PMCID: PMC2323511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.03.025
Animal models and vaccines for SARS-CoV infection
Abstract
We summarize findings of SARS-CoV infections in several animal models each of which support viral replication in lungs accompanied by histopathological changes and/or clinical signs of illness to varying degrees. New findings are reported on SARS-CoV replication and associated pathology in two additional strains (C57BL/6 and 129S6) of aged mice. We also provide new comparative data on viral replication and associated pathology following infection of golden Syrian hamsters with various SARS-CoV strains and report the levels of neutralizing antibody titers following these infections and the cross-protective efficacy of infection with these strains in protecting against heterologous challenge. Finally, we summarize findings of a variety of vaccine approaches and discuss the available in vitro and in vivo data addressing the potential for disease enhancement following re-infection in animals previously vaccinated against or infected with SARS-CoV.
Figures
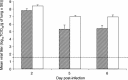
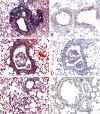
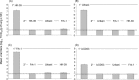
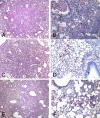
Similar articles
-
Immunization with SARS coronavirus vaccines leads to pulmonary immunopathology on challenge with the SARS virus.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35421. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035421. Epub 2012 Apr 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22536382 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in mice and hamsters of a β-propiolactone inactivated whole virus SARS-CoV vaccine.Viral Immunol. 2010 Oct;23(5):509-19. doi: 10.1089/vim.2010.0028. Viral Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20883165 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy with a severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus-neutralizing human monoclonal antibody reduces disease severity and viral burden in golden Syrian hamsters.J Infect Dis. 2006 Mar 1;193(5):685-92. doi: 10.1086/500143. Epub 2006 Jan 27. J Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16453264 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV replication and pathogenesis in an in vitro model of the human conducting airway epithelium.Virus Res. 2008 Apr;133(1):33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.03.013. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 17451829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies of SARS virus vaccines.Hong Kong Med J. 2008 Aug;14 Suppl 4:39-43. Hong Kong Med J. 2008. PMID: 18708674 Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of the current promising approaches for the development of an effective severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106928. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106928. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32862110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Responses in SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV Infections: A Comparative Review.Int J Prev Med. 2022 Mar 12;13:45. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_429_20. eCollection 2022. Int J Prev Med. 2022. PMID: 35529506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Immunology and treatment options.Clin Immunol. 2020 Jun;215:108448. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108448. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32353634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models for SARS-CoV-2 research: A comprehensive literature review.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021 Jul;68(4):1868-1885. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13907. Epub 2020 Dec 20. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021. PMID: 33128861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Long Road Toward COVID-19 Herd Immunity: Vaccine Platform Technologies and Mass Immunization Strategies.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 21;11:1817. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01817. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32793245 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bukreyev A., Lamirande E.W., Buchholz U.J., Vogel L.N., Elkins W.R., St Claire M., Murphy B.R., Subbarao K., Collins P.L. Mucosal immunisation of African green monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops) with an attenuated parainfluenza virus expressing the SARS coronavirus spike protein for the prevention of SARS. Lancet. 2004;363(9427):2122–2127. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Z., Zhang L., Qin C., Ba L., Yi C.E., Zhang F., Wei Q., He T., Yu W., Yu J., Gao H., Tu X., Gettie A., Farzan M., Yuen K.Y., Ho D.D. Recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara expressing the spike glycoprotein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus induces protective neutralizing antibodies primarily targeting the receptor binding region. J. Virol. 2005;79(5):2678–2688. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

