Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists
- PMID: 17494766
- PMCID: PMC1866313
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609699104
Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists
Abstract
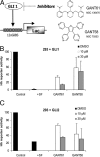
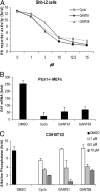
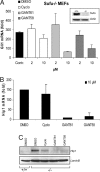
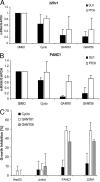
The developmentally important Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway has recently been implicated in several forms of solid cancer. Current drug development programs focus on targeting the protooncogene Smoothened, a key transmembrane pathway member. These drug candidates, albeit promising, do not address the scenario in which pathway activation occurs downstream of Smoothened, as observed in cases of medulloblastoma, glioma, pericytoma, breast cancer, and prostate cancer. A cellular screen for small-molecule antagonists of GLI-mediated transcription, which constitutes the final step in the Hh pathway, revealed two molecules that are able to selectively inhibit GLI-mediated gene transactivation. We provide genetic evidence of downstream pathway blockade by these compounds and demonstrate the ineffectiveness of upstream antagonists such as cyclopamine in such situations. Mechanistically, both inhibitors act in the nucleus to block GLI function, and one of them interferes with GLI1 DNA binding in living cells. Importantly, the discovered compounds efficiently inhibited in vitro tumor cell proliferation in a GLI-dependent manner and successfully blocked cell growth in an in vivo xenograft model using human prostate cancer cells harboring downstream activation of the Hh pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The inhibitors are the subject of a filed patent application.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone acetyltransferase PCAF is required for Hedgehog-Gli-dependent transcription and cancer cell proliferation.Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 15;73(20):6323-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4660. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23943798
-
CDK7 inhibition suppresses aberrant hedgehog pathway and overcomes resistance to smoothened antagonists.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jun 25;116(26):12986-12995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815780116. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31182587 Free PMC article.
-
Gli-1 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncology. 2006;70(5):378-89. doi: 10.1159/000098111. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Oncology. 2006. PMID: 17179732
-
Targeting GLI factors to inhibit the Hedgehog pathway.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Aug;36(8):547-58. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.05.006. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26072120 Review.
-
Interference with HH-GLI signaling inhibits prostate cancer.Trends Mol Med. 2005 May;11(5):199-203. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2005.03.004. Trends Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15882606 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular pathways: novel approaches for improved therapeutic targeting of Hedgehog signaling in cancer stem cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 1;21(3):505-13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0507. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25646180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog/GLI-mediated transcriptional activity inhibitors from Crinum asiaticum.J Nat Med. 2015 Oct;69(4):538-42. doi: 10.1007/s11418-015-0922-8. Epub 2015 May 31. J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26026497
-
Targeting the hedgehog transcription factors GLI1 and GLI2 restores sensitivity to vemurafenib-resistant human melanoma cells.Oncogene. 2017 Mar 30;36(13):1849-1861. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.348. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27748762 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog Signal Transduction: Key Players, Oncogenic Drivers, and Cancer Therapy.Dev Cell. 2016 Aug 22;38(4):333-44. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.07.026. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27554855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling inhibitors as anti-cancer agents in osteosarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2015 May 13;7(2):784-94. doi: 10.3390/cancers7020784. Cancers (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25985215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beachy PA, Karhadkar SS, Berman DM. Nature. 2004;432:324–331. - PubMed
-
- Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang B, Beachy PA, Baylin SB. Nature. 2003;422:313–317. - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Taipale J, Olson JM, et al. Science. 2002;297:1559–1561. - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes DO, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K, Parker AR, Shimada Y, Eshleman JR, Watkins DN, et al. Nature. 2003;425:846–851. - PubMed
-
- Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara S, Gardner D, Maitra A, Isaacs JT, Berman DM, Beachy PA. Nature. 2004;431:707–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

