Emi1 is needed to couple DNA replication with mitosis but does not regulate activation of the mitotic APC/C
- PMID: 17485488
- PMCID: PMC2064829
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200611166
Emi1 is needed to couple DNA replication with mitosis but does not regulate activation of the mitotic APC/C
Abstract
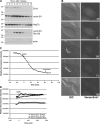
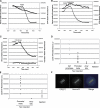
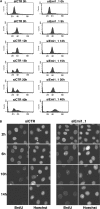
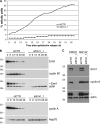
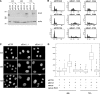
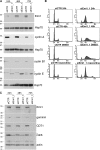
Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis is critical for the alternation between DNA replication and mitosis and for the key regulatory events in mitosis. The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is a conserved ubiquitin ligase that has a fundamental role in regulating mitosis and the cell cycle in all eukaryotes. In vertebrate cells, early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) has been proposed as an important APC/C inhibitor whose destruction may trigger activation of the APC/C at mitosis. However, in this study, we show that the degradation of Emi1 is not required to activate the APC/C in mitosis. Instead, we uncover a key role for Emi1 in inhibiting the APC/C in interphase to stabilize the mitotic cyclins and geminin to promote mitosis and prevent rereplication. Thus, Emi1 plays a crucial role in the cell cycle to couple DNA replication with mitosis, and our results also question the current view that the APC/C has to be inactivated to allow DNA replication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The APC/C inhibitor, Emi1, is essential for prevention of rereplication.Genes Dev. 2007 Jan 15;21(2):184-94. doi: 10.1101/gad.1495007. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17234884 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the role of Emi1 in the DNA replication-segregation cycle.Chromosoma. 2008 Aug;117(4):333-8. doi: 10.1007/s00412-008-0152-x. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Chromosoma. 2008. PMID: 18317792 Review.
-
Emi1 stably binds and inhibits the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome as a pseudosubstrate inhibitor.Genes Dev. 2006 Sep 1;20(17):2410-20. doi: 10.1101/gad.1454006. Epub 2006 Aug 18. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16921029 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin A2-cyclin-dependent kinase 2 cooperates with the PLK1-SCFbeta-TrCP1-EMI1-anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome axis to promote genome reduplication in the absence of mitosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(24):6500-14. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00669-09. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19822658 Free PMC article.
-
Anaphase-promoting complex-dependent proteolysis of cell cycle regulators and genomic instability of cancer cells.Oncogene. 2005 Jan 6;24(1):1-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208017. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15637585 Review.
Cited by
-
The ABBA motif binds APC/C activators and is shared by APC/C substrates and regulators.Dev Cell. 2015 Feb 9;32(3):358-372. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.01.003. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25669885 Free PMC article.
-
The spindle checkpoint, APC/C(Cdc20), and APC/C(Cdh1) play distinct roles in connecting mitosis to S phase.J Cell Biol. 2013 Jun 24;201(7):1013-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201211019. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23775192 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis ULTRAVIOLET-B-INSENSITIVE4 maintains cell division activity by temporal inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome.Plant Cell. 2011 Dec;23(12):4394-410. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.091793. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 22167059 Free PMC article.
-
Electron microscopy structure of human APC/C(CDH1)-EMI1 reveals multimodal mechanism of E3 ligase shutdown.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Jul;20(7):827-35. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2593. Epub 2013 May 26. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23708605 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct activities of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) in mouse embryonic cells.Cell Cycle. 2012 Mar 1;11(5):846-55. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.5.19251. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22333576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amon, A., S. Irniger, and K. Nasmyth. 1994. Closing the cell cycle circle in yeast: G2 cyclin proteolysis initiated at mitosis persists until the activation of G1 cyclins in the next cycle. Cell. 77:1037–1050. - PubMed
-
- Broek, D., R. Bartlett, K. Crawford, and P. Nurse. 1991. Involvement of p34cdc2 in establishing the dependency of S phase on mitosis. Nature. 349:388–393. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp, T.R., R. Bernards, and R. Agami. 2002. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 296:550–553. - PubMed
-
- Castro, A., C. Bernis, S. Vigneron, J.C. Labbe, and T. Lorca. 2005. The anaphase-promoting complex: a key factor in the regulation of cell cycle. Oncogene. 24:314–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

