Expression of lymphotoxin-alphabeta on antigen-specific T cells is required for DC function
- PMID: 17452522
- PMCID: PMC2118582
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20061968
Expression of lymphotoxin-alphabeta on antigen-specific T cells is required for DC function
Abstract
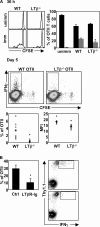
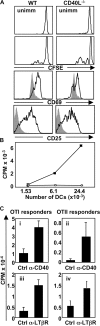
During an immune response, activated antigen (Ag)-specific T cells condition dendritic cells (DCs) to enhance DC function and survival within the inflamed draining lymph node (LN). It has been difficult to ascertain the role of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily member lymphotoxin-alphabeta (LTalphabeta) in this process because signaling through the LTbeta-receptor (LTbetaR) controls multiple aspects of lymphoid tissue organization. To resolve this, we have used an in vivo system where the expression of TNF family ligands is manipulated only on the Ag-specific T cells that interact with and condition Ag-bearing DCs. We report that LTalphabeta is a critical participant required for optimal DC function, independent of its described role in maintaining lymphoid tissue organization. In the absence of LTalphabeta or CD40L on Ag-specific T cells, DC dysfunction could be rescued in vivo via CD40 or LTbetaR stimulation, respectively, suggesting that these two pathways cooperate for optimal DC conditioning.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNF and lymphotoxin beta cooperate in the maintenance of secondary lymphoid tissue microarchitecture but not in the development of lymph nodes.J Immunol. 1999 Dec 15;163(12):6575-80. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10586051
-
LTβR and CD40: working together in dendritic cells to optimize immune responses.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):85-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01056.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017433 Review.
-
Expression of lymphotoxin beta governs immunity at two distinct levels.Eur J Immunol. 2006 Aug;36(8):2061-75. doi: 10.1002/eji.200626255. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16841297
-
The complementation of lymphotoxin deficiency with LIGHT, a newly discovered TNF family member, for the restoration of secondary lymphoid structure and function.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Jul;32(7):1969-79. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200207)32:7<1969::AID-IMMU1969>3.0.CO;2-M. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12115617
-
Biology and signal transduction pathways of the Lymphotoxin-αβ/LTβR system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011 Oct-Dec;22(5-6):301-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.11.007. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011. PMID: 22152226 Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphotoxin beta receptor signaling in intestinal epithelial cells orchestrates innate immune responses against mucosal bacterial infection.Immunity. 2010 Mar 26;32(3):403-13. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.02.011. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Immunity. 2010. PMID: 20226692 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory HVEM-BTLA pathway counter regulates lymphotoxin receptor signaling to achieve homeostasis of dendritic cells.J Immunol. 2008 Jan 1;180(1):238-48. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.1.238. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18097025 Free PMC article.
-
ICOS, CD40, and lymphotoxin beta receptors signal sequentially and interdependently to initiate a germinal center reaction.J Immunol. 2008 Feb 15;180(4):2284-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2284. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18250437 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF3 controls activation of the canonical and alternative NFkappaB by the lymphotoxin beta receptor.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):12971-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076091. Epub 2010 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20185819 Free PMC article.
-
LTβR signaling in dendritic cells induces a type I IFN response that is required for optimal clonal expansion of CD8+ T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 1;108(5):2046-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014188108. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21245292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mellman, I., and R.M. Steinman. 2001. Dendritic cells: specialized and regulated antigen processing machines. Cell. 106:255–258. - PubMed
-
- Quezada, S.A., L.Z. Jarvinen, E.F. Lind, and R.J. Noelle. 2004. CD40/CD154 interactions at the interface of tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:307–328. - PubMed
-
- Schulz, O., A.D. Edwards, M. Schito, J. Aliberti, S. Manickasingham, A. Sher, and C. Reis e Sousa. 2000. CD40 triggering of heterodimeric IL-12 p70 production by dendritic cells in vivo requires a microbial priming signal. Immunity. 13:453–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

