Phosphorylation of CBP by IKKalpha promotes cell growth by switching the binding preference of CBP from p53 to NF-kappaB
- PMID: 17434128
- PMCID: PMC2312502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.02.019
Phosphorylation of CBP by IKKalpha promotes cell growth by switching the binding preference of CBP from p53 to NF-kappaB
Abstract
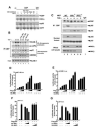
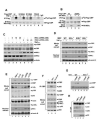
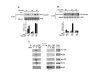
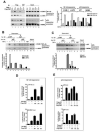
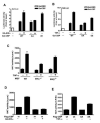
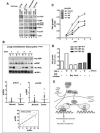
CBP plays a central role in coordinating and integrating multiple signaling pathways. Competition between NF-kappaB and p53 for CBP is a crucial determinant of whether a cell proliferates or undergoes apoptosis. However, how the CBP-dependent crosstalk between these two transcription factors is regulated remains unclear. Here, we show that IKKalpha phosphorylates CBP at serine 1382 and serine 1386 and consequently increases CBP's HAT and transcriptional activities. Importantly, such phosphorylation enhances NF-kappaB-mediated gene expression and suppresses p53-mediated gene expression by switching the binding preference of CBP from p53 to NF-kappaB, thus promoting cell growth. The CBP phosphorylation also correlates with constitutive IKKalpha activation in human lung tumor tissue compared with matched nontumor lung tissue. Our results suggest that phosphorylation of CBP by IKKalpha regulates the CBP-mediated crosstalk between NF-kappaB and p53 and thus may be a critical factor in the promotion of cell proliferation and tumor growth.
Figures

Comment in
-
p53 and NF-kappaB crosstalk: IKKalpha tips the balance.Mol Cell. 2007 Apr 27;26(2):158-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.04.006. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17466617 Review.
Similar articles
-
p53 and NF-kappaB crosstalk: IKKalpha tips the balance.Mol Cell. 2007 Apr 27;26(2):158-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.04.006. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17466617 Review.
-
Activated p53 induces NF-kappaB DNA binding but suppresses its transcriptional activation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Jul 18;372(1):137-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.05.021. Epub 2008 May 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18477470
-
HIV-1 Tat protein induces IL-10 production in monocytes by classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways.Eur J Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;87(12):947-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.06.005. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18760861
-
Protein kinase C delta activates IkappaB-kinase alpha to induce the p53 tumor suppressor in response to oxidative stress.Cell Signal. 2007 Oct;19(10):2088-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jun 21. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17644309
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 modulates distinctive NF- kappaB pathways through C-terminus-activating region 1 to regulate epidermal growth factor receptor expression.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(13):6605-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00344-10. Epub 2010 Apr 21. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20410275 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA targets in immune genes and the Dicer/Argonaute and ARE machinery components.Mol Immunol. 2008 Apr;45(7):1995-2006. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.10.035. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18061676 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB inducing kinase, NIK mediates cigarette smoke/TNFα-induced histone acetylation and inflammation through differential activation of IKKs.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023488. Epub 2011 Aug 24. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887257 Free PMC article.
-
FK506-binding protein 51 is a possible novel tumoral marker.Cell Death Dis. 2010 Jul 15;1(7):e55. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2010.32. Cell Death Dis. 2010. PMID: 21364660 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B enhances the tumor growth of ovarian cancer cell line derived from a low-grade papillary serous carcinoma in p53-independent pathway.BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 2;16:582. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2617-2. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27484466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ait-Si-Ali S, Carlisi D, Ramirez S, Upegui-Gonzalez LC, Duquet A, Robin P, Rudkin B, Harel-Bellan A, Trouche D. Phosphorylation by p44 MAP Kinase/ERK1 stimulates CBP histone acetyl transferase activity in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999;262:157–162. - PubMed
-
- Anest V, Cogswell PC, Baldwin AS., Jr. IkappaB kinase alpha and p65/RelA contribute to optimal epidermal growth factor-induced c-fos gene expression independent of IkappaBalpha degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:31183–31189. - PubMed
-
- Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS. A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature. 2003;423:659–663. - PubMed
-
- Avantaggiati ML, Ogryzko V, Gardner K, Giordano A, Levine AS, Kelly K. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell. 1997;89:1175–1184. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature. 1996;384:641–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

