Beta-catenin regulates acetylcholine receptor clustering in muscle cells through interaction with rapsyn
- PMID: 17428970
- PMCID: PMC6672526
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4691-06.2007
Beta-catenin regulates acetylcholine receptor clustering in muscle cells through interaction with rapsyn
Abstract
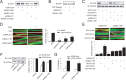
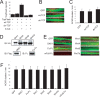
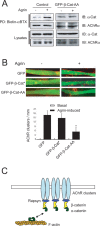
Agrin is believed to be a factor used by motoneurons to direct acetylcholine receptor (AChR) clustering at the neuromuscular junction. However, exactly how agrin mediates this effect remains unclear. Here we demonstrate that the beta-catenin interacts with rapsyn, a molecule key for AChR clustering. Agrin stimulation increases the association of beta-catenin with surface AChRs. Suppression of beta-catenin expression inhibited agrin-induced AChR clustering, suggesting a necessary role of beta-catenin in this event. The beta-catenin action did not appear to require the function of T-cell factors (TCFs), suggesting a mechanism independent of TCF-mediated transcription. In contrast, prevention of beta-catenin from interacting with alpha-catenin attenuated agrin-induced AChR clustering. These results suggest that beta-catenin may serve as a link between AChRs and alpha-catenin-associated cytoskeleton, revealing a novel function of beta-catenin in synaptogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural agrin increases postsynaptic ACh receptor packing by elevating rapsyn protein at the mouse neuromuscular synapse.Dev Neurobiol. 2008 Aug;68(9):1153-69. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20654. Dev Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18506821
-
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling suppresses Rapsyn expression and inhibits acetylcholine receptor clustering at the neuromuscular junction.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 1;283(31):21668-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709939200. Epub 2008 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18541538
-
Agrin regulates rapsyn interaction with surface acetylcholine receptors, and this underlies cytoskeletal anchoring and clustering.J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 28;278(9):7350-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210865200. Epub 2002 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12486121
-
Acetylcholine receptors and the cytoskeletal connection.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1995 Dec;22(12):961-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1995.tb02333.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1995. PMID: 8846518 Review.
-
Recombinant neuromuscular synapses.Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):671-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141005. Bioessays. 1992. PMID: 1365879 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of Rapsyn in neuromuscular junction and congenital myasthenic syndrome.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Sep 4;23(5):772-784. doi: 10.17305/bb.2022.8641. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36815443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Adult Skeletal Muscles, the Co-Receptors of Canonical Wnt Signaling, Lrp5 and Lrp6, Determine the Distribution and Size of Fiber Types, and Structure and Function of Neuromuscular Junctions.Cells. 2022 Dec 8;11(24):3968. doi: 10.3390/cells11243968. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36552732 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine activates YAP1 through nAChRs mediated signaling in esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC).PLoS One. 2014 Mar 12;9(3):e90836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090836. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24621512 Free PMC article.
-
The YAP1/TAZ-TEAD transcriptional network regulates gene expression at neuromuscular junctions in skeletal muscle fibers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 25;52(2):600-624. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1124. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38048326 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90 beta regulates rapsyn turnover and subsequent AChR cluster formation and maintenance.Neuron. 2008 Oct 9;60(1):97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.08.013. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18940591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberle H, Schwartz H, Hoschuetzky H, Kemler R. Single amino acid substitutions in proteins of the armadillo gene family abolish their binding to alpha-catenin. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:1520–1526. - PubMed
-
- Apel ED, Glass DJ, Moscoso LM, Yancopoulos GD, Sanes JR. Rapsyn is required for MuSK signaling and recruits synaptic components to a MuSK-containing scaffold. Neuron. 1997;18:623–635. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1996;382:638–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
