Intranuclear targeting and nuclear export of the adenovirus E1B-55K protein are regulated by SUMO1 conjugation
- PMID: 17428914
- PMCID: PMC1871846
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0702158104
Intranuclear targeting and nuclear export of the adenovirus E1B-55K protein are regulated by SUMO1 conjugation
Abstract
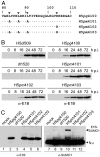
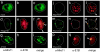
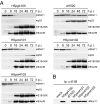
We have investigated the requirements for CRM1-mediated nuclear export and SUMO1 conjugation of the adenovirus E1B-55K protein during productive infection. Our data show that CRM1 is the major export receptor for E1B-55K in infected cells. Functional inactivation of the E1B-55K CRM1-dependent nuclear export signal (NES) or leptomycin B treatment causes an almost complete redistribution of the viral protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and its accumulation at the periphery of the viral replication centers. Interestingly, however, this nuclear restriction imposed on the wild type and the NES mutant protein is fully compensated by concurrent inactivation of the adjacent SUMO1 conjugation site. Moreover, the same mutation fully reverses defects of the NES mutant in the nucleocytoplasmic transport of Mre11 and proteasomal degradation of p53. These results show that nuclear export of E1B-55K in infected cells occurs via CRM1-dependent and -independent pathways and suggest that SUMO1 conjugation and deconjugation provide a molecular switch that commits E1B-55K to a CRM1-independent export pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The adenovirus type 5 E1B-55K oncoprotein actively shuttles in virus-infected cells, whereas transport of E4orf6 is mediated by a CRM1-independent mechanism.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(12):5677-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.12.5677-5683.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11356976 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of single-amino-acid substitution mutants of adenovirus type 5 E1B-55K protein.J Virol. 2001 May;75(9):4297-307. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.9.4297-4307.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11287579 Free PMC article.
-
The adenovirus type 5 E1B-55K oncoprotein is a highly active shuttle protein and shuttling is independent of E4orf6, p53 and Mdm2.Oncogene. 2000 Feb 17;19(7):850-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203395. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10702793
-
The biology of the adenovirus E1B 55K protein.FEBS Lett. 2019 Dec;593(24):3504-3517. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13694. Epub 2019 Dec 8. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 31769868 Review.
-
Interactions between adenovirus proteins and the p53 pathway: the development of ONYX-015.Semin Cancer Biol. 2000 Dec;10(6):453-9. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2000.0336. Semin Cancer Biol. 2000. PMID: 11170867 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of E1B55K in E4orf6/E1B55K E3 ligase complexes formed by different human adenovirus serotypes.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6232-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00384-13. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23536656 Free PMC article.
-
Human Adenovirus Type 5 Infection Leads to Nuclear Envelope Destabilization and Membrane Permeability Independently of Adenovirus Death Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 2;22(23):13034. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313034. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884837 Free PMC article.
-
SPOC1-mediated antiviral host cell response is antagonized early in human adenovirus type 5 infection.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(11):e1003775. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003775. Epub 2013 Nov 21. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24278021 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Mimicry to Usurp Ubiquitin and SUMO Host Pathways.Viruses. 2015 Aug 28;7(9):4854-72. doi: 10.3390/v7092849. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26343706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus proteins with SUMO-conjugating enzyme reveals the SUMOylation of nucleocapsid protein.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 13;12(12):e0189191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189191. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29236778 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

