Effects of apoE genotype on macrophage inflammation and heme oxygenase-1 expression
- PMID: 17416347
- PMCID: PMC2096715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.03.150
Effects of apoE genotype on macrophage inflammation and heme oxygenase-1 expression
Abstract
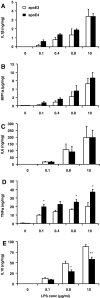
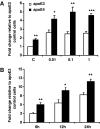
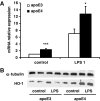
In order to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the aetiology of apolipoprotein E4 genotype-cardiovascular disease (CVD) associations, the impact of the apoE genotype on the macrophage inflammatory response was examined. The murine monocyte-macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7) stably transfected to produce equal amounts of human apoE3 or apoE4 was used. Following LPS stimulation, apoE4-macrophages showed higher and lower concentrations of tumour necrosis factor alpha (pro-inflammatory) and interleukin 10 (anti-inflammatory), respectively, both at mRNA and protein levels. In addition, increased expression of heme oxygenase-1 (a stress-induced anti-inflammatory protein) was observed in the apoE4-cells. Furthermore, in apoE4-macrophages, an enhanced transactivation of the key redox sensitive transcription factor NF-kappaB was shown. Current data indicate that apoE4 macrophages have an altered inflammatory response, which may contribute to the higher CVD risk observed in apoE4 carriers.
Figures
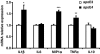
Similar articles
-
Implications of apolipoprotein E genotype on inflammation and vitamin E status.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010 May;54(5):623-30. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900398. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010. PMID: 20183830 Review.
-
Effect of apoE genotype and vitamin E on biomarkers of oxidative stress in cultured neuronal cells and the brain of targeted replacement mice.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;58(4):683-98. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 18195481
-
Influence of apolipoprotein E genotype and dietary alpha-tocopherol on redox status and C-reactive protein levels in apolipoprotein E3 and E4 targeted replacement mice.Br J Nutr. 2008 Jul;100(1):44-53. doi: 10.1017/S000711450788634X. Epub 2008 Jan 8. Br J Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18179727
-
Sex steroids, APOE genotype and the innate immune system.Neurobiol Aging. 2005 Mar;26(3):363-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.08.001. Neurobiol Aging. 2005. PMID: 15639315 Review.
-
Differential effects of apolipoprotein E3 and E4 on markers of oxidative status in macrophages.Br J Nutr. 2007 May;97(5):864-71. doi: 10.1017/S0007114507669219. Br J Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17381973
Cited by
-
Evidence from case-control and longitudinal studies supports associations of genetic variation in APOE, CETP, and IL6 with human longevity.Age (Dordr). 2013 Apr;35(2):487-500. doi: 10.1007/s11357-011-9373-7. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Age (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 22234866 Free PMC article.
-
Creating an atlas of the bone microenvironment during oral inflammatory-related bone disease using single-cell profiling.Elife. 2023 Feb 1;12:e82537. doi: 10.7554/eLife.82537. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36722472 Free PMC article.
-
Heme oxygenase-1 dysregulation in the brain: implications for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.Curr HIV Res. 2014;12(3):174-88. doi: 10.2174/1570162x12666140526122709. Curr HIV Res. 2014. PMID: 24862327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose-dependent role of claudin-1 in vivo in orchestrating features of atopic dermatitis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 12;113(28):E4061-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525474113. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27342862 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E inhibits toll-like receptor (TLR)-3- and TLR-4-mediated macrophage activation through distinct mechanisms.Biochem J. 2010 Apr 28;428(1):47-54. doi: 10.1042/BJ20100016. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20218969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eichner J.E., Dunn S.T., Perveen G., Thompson D.M., Stewart K.E., Stroehla B.C. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and cardiovascular disease: a HuGE review. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002;155:487–495. - PubMed
-
- Song Y., Stampfer M.J., Liu S. Meta-analysis: apolipoprotein E genotypes and risk for coronary heart disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004;141:137–147. - PubMed
-
- Minihane A.M., Jofre-Monseny L., Olano-Martin E., Rimbach G. ApoE genotype, cardiovascular risk and responsiveness to dietary fat manipulation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007;66:183–197. - PubMed
-
- Kayden H.J., Maschio F., Traber M.G. The secretion of apolipoprotein E by human monocyte-derived macrophages. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1985;239:388–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

