Structure-activity relationship of uridine 5'-diphosphoglucose analogues as agonists of the human P2Y14 receptor
- PMID: 17407275
- PMCID: PMC3408610
- DOI: 10.1021/jm061222w
Structure-activity relationship of uridine 5'-diphosphoglucose analogues as agonists of the human P2Y14 receptor
Abstract
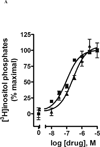
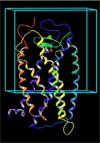
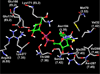
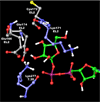
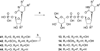
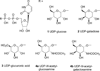
UDP-glucose (UDPG) and derivatives are naturally occurring agonists of the Gi protein-coupled P2Y14 receptor, which occurs in the immune system. We synthesized and characterized pharmacologically novel analogues of UDPG modified on the nucleobase, ribose, and glucose moieties, as the basis for designing novel ligands in conjunction with modeling. The recombinant human P2Y14 receptor expressed in COS-7 cells was coupled to phospholipase C through an engineered Galpha-q/i protein. Most modifications of the uracil or ribose moieties abolished activity; this is among the least permissive P2Y receptors. However, a 2-thiouracil modification in 15 (EC50 49 +/- 2 nM) enhanced the potency of UDPG (but not UDP-glucuronic acid) by 7-fold. 4-Thio analogue 13 was equipotent to UDPG, but S-alkylation was detrimental. Compound 15 was docked in a rhodposin-based receptor homology model, which correctly predicted potent agonism of UDP-fructose, UDP-mannose, and UDP-inositol. The hexose moiety of UDPG interacts with multiple H-bonding and charged residues and provides a fertile region for agonist modification.
Figures


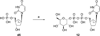
Similar articles
-
Human P2Y(14) receptor agonists: truncation of the hexose moiety of uridine-5'-diphosphoglucose and its replacement with alkyl and aryl groups.J Med Chem. 2010 Jan 14;53(1):471-80. doi: 10.1021/jm901432g. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 19902968 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular recognition in the P2Y(14) receptor: Probing the structurally permissive terminal sugar moiety of uridine-5'-diphosphoglucose.Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Jul 15;17(14):5298-311. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.05.024. Epub 2009 May 15. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19502066 Free PMC article.
-
UDP-glucose acting at P2Y14 receptors is a mediator of mast cell degranulation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Mar 15;79(6):873-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.10.024. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19896471 Free PMC article.
-
UDP-glucose sensing P2Y14R: A novel target for inflammation.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Nov 1;238:109655. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109655. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37423482 Review.
-
P2 receptors activated by uracil nucleotides--an update.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(3):289-312. doi: 10.2174/092986706775476052. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16475938 Review.
Cited by
-
The nucleotide sugar UDP-glucose mobilizes long-term repopulating primitive hematopoietic cells.J Clin Invest. 2013 Aug;123(8):3420-35. doi: 10.1172/JCI64060. Epub 2013 Jul 25. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23863713 Free PMC article.
-
Selective induction of P2Y14 receptor by RANKL promotes osteoclast formation.Mol Cells. 2013 Sep;36(3):273-7. doi: 10.1007/s10059-013-0226-3. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Mol Cells. 2013. PMID: 24048691 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, pharmacological characterization of a fluorescent agonist of the P2Y₁₄ receptor.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Nov 1;25(21):4733-4739. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.08.021. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 26303895 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y receptors in the mammalian nervous system: pharmacology, ligands and therapeutic potential.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Sep;11(6):722-38. doi: 10.2174/187152712803581047. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22963441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signalling and pharmacological properties of the P2Y receptor.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2010 Jun;199(2):149-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02116.x. Epub 2010 Mar 24. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2010. PMID: 20345417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- North RA, Barnard EA. Nucleotide receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1997;7:346–357. - PubMed
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Fumagalli M, King BF, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA. International Union of Pharmacology. Update of the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006;58:281–341. - PMC - PubMed
-
- von Kügelgen I. Pharmacological profiles of cloned mammalian P2Y-receptor subtypes. Pharmacology Therapeutics. 2006;110:415–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

