Upregulation of Twist-1 by NF-kappaB blocks cytotoxicity induced by chemotherapeutic drugs
- PMID: 17403902
- PMCID: PMC1900008
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01219-06
Upregulation of Twist-1 by NF-kappaB blocks cytotoxicity induced by chemotherapeutic drugs
Abstract
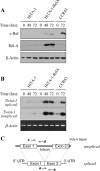
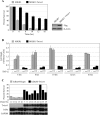
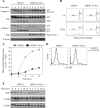
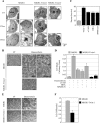
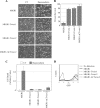
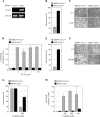
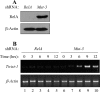
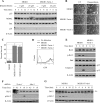
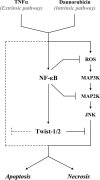
NF-kappaB/Rel transcription factors are central to controlling programmed cell death (PCD). Activation of NF-kappaB blocks PCD induced by numerous triggers, including ligand engagement of tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R) family receptors. The protective activity of NF-kappaB is also crucial for oncogenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Downstream of TNF-Rs, this activity of NF-kappaB has been linked to the suppression of reactive oxygen species and the c-Jun-N-terminal-kinase (JNK) cascade. The mechanism by which NF-kappaB inhibits PCD triggered by chemotherapeutic drugs, however, remains poorly understood. To understand this mechanism, we sought to identify unrecognized protective genes that are regulated by NF-kappaB. Using an unbiased screen, we identified the basic-helix-loop-helix factor Twist-1 as a new mediator of the protective function of NF-kappaB. Twist-1 is an evolutionarily conserved target of NF-kappaB, blocks PCD induced by chemotherapeutic drugs and TNF-alpha in NF-kappaB-deficient cells, and is essential to counter this PCD in cancer cells. The protective activity of Twist-1 seemingly halts PCD independently of interference with cytotoxic JNK, p53, and p19(ARF) signaling, suggesting that it mediates a novel protective mechanism activated by NF-kappaB. Indeed, our data indicate that this activity involves a control of inhibitory Bcl-2 phosphorylation. The data also suggest that Twist-1 and -2 play an important role in NF-kappaB-dependent chemoresistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The NF-kappaB-mediated control of the JNK cascade in the antagonism of programmed cell death in health and disease.Cell Death Differ. 2006 May;13(5):712-29. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401865. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16456579 Review.
-
Induction of gadd45beta by NF-kappaB downregulates pro-apoptotic JNK signalling.Nature. 2001 Nov 15;414(6861):308-13. doi: 10.1038/35104560. Nature. 2001. PMID: 11713530
-
Regulation of death receptor expression and TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB.Nat Cell Biol. 2001 Apr;3(4):409-16. doi: 10.1038/35070096. Nat Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11283615
-
N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide inhibits invasion, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and potentiates apoptosis through down-regulation of I(kappa)B(alpha) kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products.Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 15;65(20):9555-65. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1585. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16230421
-
Linking JNK signaling to NF-kappaB: a key to survival.J Cell Sci. 2004 Oct 15;117(Pt 22):5197-208. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01483. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15483317 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of the Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor 1 (BRMS1) maintains in vitro chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2009 Aug 18;281(1):100-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.035. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 19307053 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Molecular Markers for Breast Cancer.Biomark Cancer. 2016 Mar 13;8:25-42. doi: 10.4137/BIC.S38394. eCollection 2016. Biomark Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26997872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Twist2 is a valuable prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Apr 21;19(15):2404-11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2404. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23613636 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits nasopharyngeal cancer stem cell self-renewal and migration and reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via NF-κB p65 inactivation.Tumour Biol. 2015 Apr;36(4):2747-61. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2899-4. Epub 2014 Dec 7. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25487615
-
Sustained activation of NF-κB through constitutively active IKKβ leads to senescence bypass in murine dermal fibroblasts.Cell Cycle. 2024 Feb;23(3):308-327. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2024.2325802. Epub 2024 Mar 10. Cell Cycle. 2024. PMID: 38461418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basu, A., G. DuBois, and S. Haldar. 2006. Posttranslational modifications of Bcl2 family members—a potential therapeutic target for human malignancy. Front. Biosci. 11:1508-1521. - PubMed
-
- Carroll, A. G., H. J. Voeller, L. Sugars, and E. P. Gelmann. 1993. p53 oncogene mutations in three human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate 23:123-134. - PubMed
-
- Castanon, I., and M. Baylies. 2002. A twist in fate: evolutionary comparison of Twist structure and function. Gene 287:11-22. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Z. F., and R. R. Behringer. 1995. twist is required in head mesenchyme for cranial neural tube morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 9:686-699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
