Selective requirement for SAGA in Hog1-mediated gene expression depending on the severity of the external osmostress conditions
- PMID: 17403898
- PMCID: PMC1900016
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00089-07
Selective requirement for SAGA in Hog1-mediated gene expression depending on the severity of the external osmostress conditions
Abstract
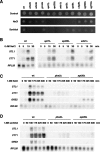
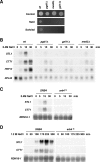
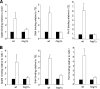
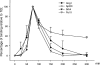
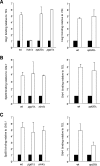
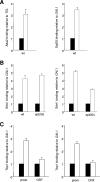
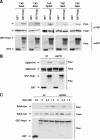
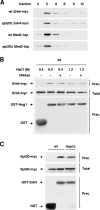
Regulation of gene expression by the Hog1 stress-activated protein kinase is essential for proper cell adaptation to osmostress. Hog1 coordinates an extensive transcriptional program through the modulation of transcription. To identify systematically novel components of the transcriptional machinery required for osmostress-mediated gene expression, we performed an exhaustive genome-wide genetic screening, searching for mutations that render cells osmosensitive at high osmolarity and that are associated with reduced expression of osmoresponsive genes. The SAGA and Mediator complexes were identified as putative novel regulators of osmostress-mediated transcription. Interestingly, whereas Mediator is essential for osmostress gene expression, the requirement for SAGA is different depending on the strength of the extracellular osmotic conditions. At mild osmolarity, SAGA mutants show only very slight defects on RNA polymerase II (Pol II) recruitment and gene expression, whereas at severe osmotic conditions, SAGA mutants show completely impaired RNA Pol II recruitment and transcription of osmoresponsive genes. Thus, our results define an essential role for Mediator in osmostress gene expression and a selective role for SAGA under severe osmostress. Our results indicate that the requirement for a transcriptional complex to regulate a promoter might be determined by the strength of the stimuli perceived by the cell through the regulation of interactions between transcriptional complexes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Osmostress-induced transcription by Hot1 depends on a Hog1-mediated recruitment of the RNA Pol II.EMBO J. 2003 May 15;22(10):2433-42. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg243. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12743037 Free PMC article.
-
The MAPK Hog1 recruits Rpd3 histone deacetylase to activate osmoresponsive genes.Nature. 2004 Jan 22;427(6972):370-4. doi: 10.1038/nature02258. Nature. 2004. PMID: 14737171
-
The stress-activated Hog1 kinase is a selective transcriptional elongation factor for genes responding to osmotic stress.Mol Cell. 2006 Jul 21;23(2):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.05.031. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16857590
-
Osmostress-induced gene expression--a model to understand how stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs) regulate transcription.FEBS J. 2015 Sep;282(17):3275-85. doi: 10.1111/febs.13323. Epub 2015 Jun 10. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25996081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward a genomic view of the gene expression program regulated by osmostress in yeast.OMICS. 2010 Dec;14(6):619-27. doi: 10.1089/omi.2010.0046. Epub 2010 Aug 20. OMICS. 2010. PMID: 20726780 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering dynamic dose responses of natural promoters and single cis elements upon osmotic and oxidative stress in yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(11):2228-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00240-13. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23530054 Free PMC article.
-
High-confidence mapping of chemical compounds and protein complexes reveals novel aspects of chemical stress response in yeast.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Jan;6(1):175-81. doi: 10.1039/b911821g. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20024079 Free PMC article.
-
High throughput protein-protein interaction data: clues for the architecture of protein complexes.Proteome Sci. 2008 Nov 26;6:32. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-6-32. Proteome Sci. 2008. PMID: 19032795 Free PMC article.
-
The human SPT20-containing SAGA complex plays a direct role in the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;29(6):1649-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01076-08. Epub 2008 Dec 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19114550 Free PMC article.
-
Med3-mediated NADPH generation to help Saccharomyces cerevisiae tolerate hyperosmotic stress.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Aug 21;90(8):e0096824. doi: 10.1128/aem.00968-24. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39082808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alepuz, P. M., A. Jovanovic, V. Reiser, and G. Ammerer. 2001. Stress-induced map kinase Hog1 is part of transcription activation complexes. Mol. Cell 7:767-777. - PubMed
-
- Andrau, J. C., L. van de Pasch, P. Lijnzaad, T. Bijma, M. G. Koerkamp, J. van de Peppel, M. Werner, and F. C. Holstege. 2006. Genome-wide location of the coactivator mediator: binding without activation and transient Cdk8 interaction on DNA. Mol. Cell 22:179-192. - PubMed
-
- Bryant, G. O., and M. Ptashne. 2003. Independent recruitment in vivo by Gal4 of two complexes required for transcription. Mol. Cell 11:1301-1309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
