Distance constraints between microRNA target sites dictate efficacy and cooperativity
- PMID: 17389647
- PMCID: PMC1874663
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm133
Distance constraints between microRNA target sites dictate efficacy and cooperativity
Abstract
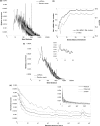
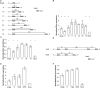
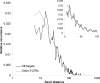
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have the potential to regulate the expression of thousands of genes, but the mechanisms that determine whether a gene is targeted or not are poorly understood. We studied the genomic distribution of distances between pairs of identical miRNA seeds and found a propensity for moderate distances greater than about 13 nt between seed starts. Experimental data show that optimal down-regulation is obtained when two seed sites are separated by between 13 and 35 nt. By analyzing the distance between seed sites of endogenous miRNAs and transfected small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), we also find that cooperative targeting of sites with a separation in the optimal range can explain some of the siRNA off-target effects that have been reported in the literature.
Figures
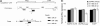
Similar articles
-
A detailed investigation of accessibilities around target sites of siRNAs and miRNAs.Bioinformatics. 2011 Jul 1;27(13):1788-97. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr276. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21531769
-
Determinants of targeting by endogenous and exogenous microRNAs and siRNAs.RNA. 2007 Nov;13(11):1894-910. doi: 10.1261/rna.768207. Epub 2007 Sep 13. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17872505 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of putative miRNA binding sites and mRNA 3' ends as targets for siRNA-mediated gene knockdown.Oligonucleotides. 2009 Mar;19(1):41-52. doi: 10.1089/oli.2008.0154. Oligonucleotides. 2009. PMID: 19196098
-
MicroRNAs--targeting and target prediction.N Biotechnol. 2010 Jul 31;27(3):243-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2010.02.016. Epub 2010 Feb 26. N Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20219708 Review.
-
Prediction of human microRNA targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:101-13. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:101. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957370 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of GB virus B RNA abundance by microRNA-122: dependence on and escape from microRNA-122 restriction.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(13):7338-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00378-13. Epub 2013 Apr 24. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23616647 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate transcriptome-wide prediction of microRNA targets and small interfering RNA off-targets with MIRZA-G.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 18;43(3):1380-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv050. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25628353 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic characterization of seed overlap microRNA cotargeting associated with lupus pathogenesis.BMC Biol. 2022 Nov 11;20(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01447-4. BMC Biol. 2022. PMID: 36357926 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of microRNA function in animals.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Jan;20(1):21-37. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0045-7. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30108335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outside the limit: questioning the distance restrictions for cooperative miRNA binding sites.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Jan 24;28(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00421-4. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36694129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–858. - PubMed
-
- Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–862. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:862–864. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature. 2005;435:839–843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

